Bagged vacuums offer superior filtration by trapping dust and allergens in disposable bags, making them ideal for allergy sufferers. Bagless vacuums provide convenience and cost savings by eliminating the need for replacement bags, with easy-to-empty dustbins. Choosing between the two depends on preferences for maintenance, filtration efficiency, and long-term operating costs.
Table of Comparison
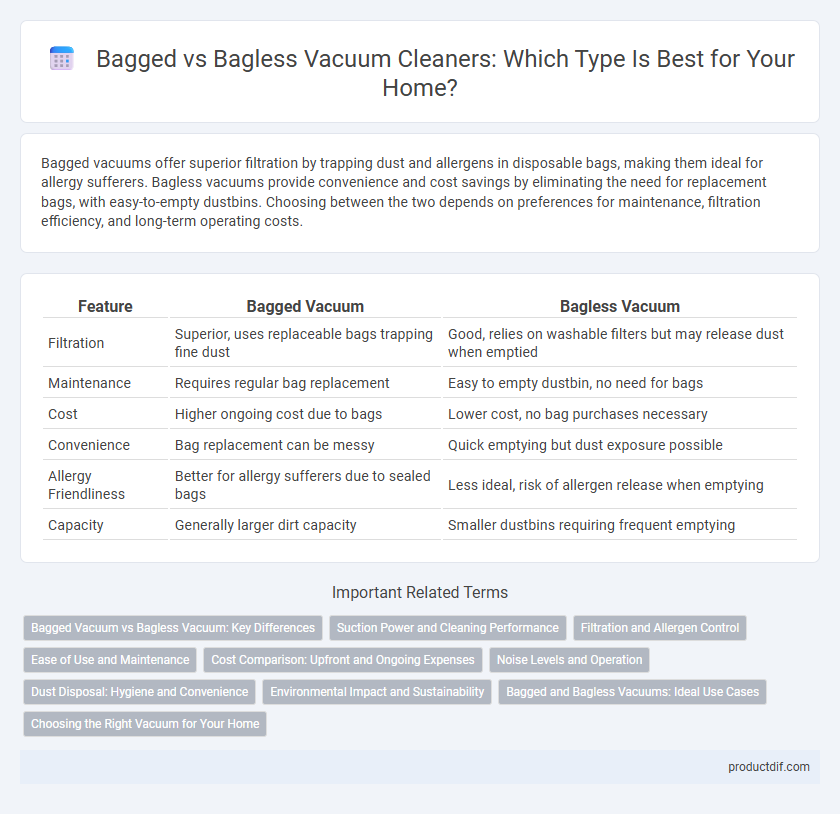
| Feature | Bagged Vacuum | Bagless Vacuum |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration | Superior, uses replaceable bags trapping fine dust | Good, relies on washable filters but may release dust when emptied |
| Maintenance | Requires regular bag replacement | Easy to empty dustbin, no need for bags |
| Cost | Higher ongoing cost due to bags | Lower cost, no bag purchases necessary |
| Convenience | Bag replacement can be messy | Quick emptying but dust exposure possible |
| Allergy Friendliness | Better for allergy sufferers due to sealed bags | Less ideal, risk of allergen release when emptying |
| Capacity | Generally larger dirt capacity | Smaller dustbins requiring frequent emptying |
Bagged Vacuum vs Bagless Vacuum: Key Differences
Bagged vacuums use replaceable bags to collect dust and debris, providing superior filtration and reducing allergens, making them ideal for allergy sufferers. Bagless vacuums feature a transparent dirt canister that allows easy monitoring of dirt levels and reduce ongoing costs by eliminating the need for bags. However, bagless models often require more frequent emptying and cleaning, while bagged vacuums typically offer more powerful suction and less maintenance.
Suction Power and Cleaning Performance
Bagged vacuums typically maintain consistent suction power over time due to their ability to trap dust and debris effectively, preventing clogging and airflow loss. Bagless vacuums often experience a gradual decrease in suction strength as filters and dust compartments fill, which can impact overall cleaning performance. For optimal cleaning efficiency, bagged models generally outperform bagless units in sustained suction power and debris containment.
Filtration and Allergen Control
Bagged vacuums excel in filtration by trapping dust, pollen, and allergens within sealed bags, preventing their release back into the air and enhancing indoor air quality. Bagless vacuums rely on cyclonic technology and washable filters to capture particles, but may require frequent maintenance to maintain effective allergen control. For individuals with allergies or asthma, bagged vacuums often provide superior contamination containment and help reduce airborne allergens more effectively.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Bagged vacuums offer easy maintenance with disposable bags that prevent dust exposure during disposal, making them ideal for allergy sufferers. Bagless vacuums require frequent emptying and filter cleaning but provide cost savings by eliminating the need for replacement bags. Ease of use varies as bagged models tend to have larger dust capacities, reducing the frequency of emptying compared to bagless systems.
Cost Comparison: Upfront and Ongoing Expenses
Bagged vacuums typically have a higher upfront cost due to the need for specialized filters and bags but tend to have lower maintenance requirements, reducing the frequency of part replacements. Bagless vacuums offer a lower initial purchase price but may involve ongoing expenses related to filter replacements and occasional component cleanings. Considering the total cost of ownership, bagged models often incur steady but predictable costs, while bagless options might fluctuate depending on usage and filter quality.
Noise Levels and Operation
Bagged vacuums generally operate more quietly due to their sealed design that minimizes airflow noise and vibration during use. Bagless vacuums often produce louder sounds as the motor struggles with dust and debris directly impacting the filter, increasing operational noise. Choosing between the two depends on balancing noise tolerance with convenience and maintenance preferences.
Dust Disposal: Hygiene and Convenience
Bagged vacuums trap dust and allergens inside sealed bags, ensuring hygienic disposal without releasing particles back into the air, ideal for allergy sufferers. Bagless vacuums use a dirt bin that can be emptied quickly without purchasing replacement bags, offering convenience but requiring careful emptying to avoid dust exposure. Choosing between the two depends on balancing ease of use with maintaining clean air quality during dust disposal.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bagged vacuums generate more waste due to disposable bags that contribute to landfill accumulation, whereas bagless models reduce plastic waste by eliminating the need for bags, promoting environmental sustainability. However, bagless vacuums require frequent filter replacements, which can offset some sustainability benefits if filters are not recyclable. Choosing vacuums with reusable or biodegradable bags and energy-efficient motors enhances eco-friendly cleaning practices in households.
Bagged and Bagless Vacuums: Ideal Use Cases
Bagged vacuums excel in environments with high dust and allergen levels, as their sealed bags trap particles effectively, making them ideal for allergy sufferers and large homes. Bagless vacuums offer convenience and eco-friendliness, perfect for smaller spaces or households seeking easy maintenance without the recurring cost of replacement bags. Choosing between bagged and bagless vacuums depends on factors like cleaning frequency, sensitivity to allergens, and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Vacuum for Your Home
Bagged vacuums offer superior filtration and allergen containment, making them ideal for homes with allergy sufferers or pets. Bagless vacuums provide convenience and cost savings by eliminating the need to purchase replacement bags, but they may require more frequent filter maintenance. Evaluating your home's cleaning needs, budget, and air quality concerns will help determine the best vacuum type for effective dust and debris removal.
Bagged Vacuum vs Bagless Vacuum Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com