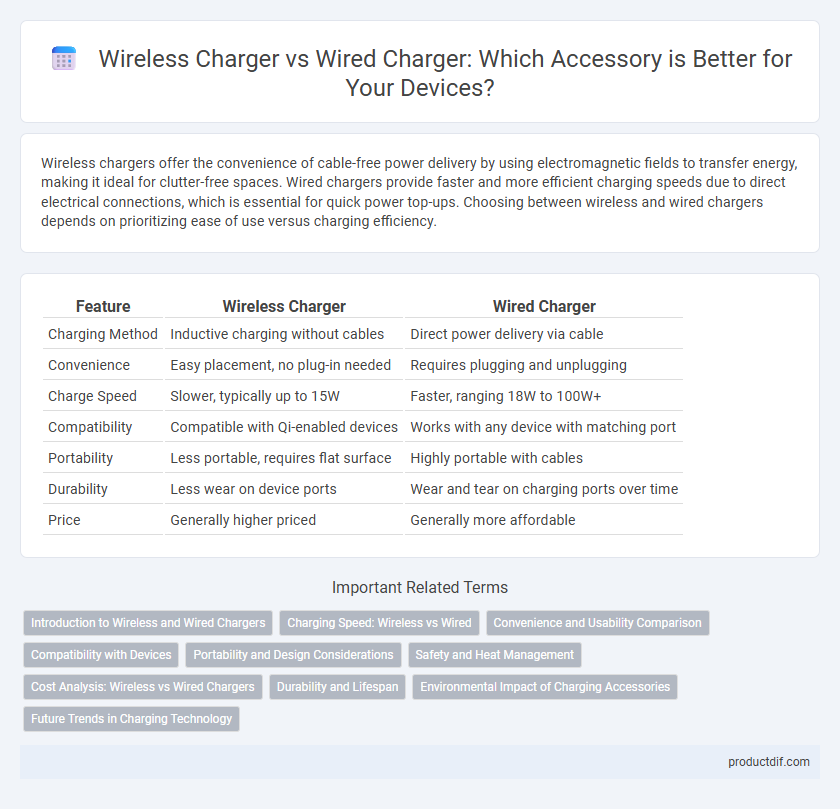
Wireless chargers offer the convenience of cable-free power delivery by using electromagnetic fields to transfer energy, making it ideal for clutter-free spaces. Wired chargers provide faster and more efficient charging speeds due to direct electrical connections, which is essential for quick power top-ups. Choosing between wireless and wired chargers depends on prioritizing ease of use versus charging efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wireless Charger | Wired Charger |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Method | Inductive charging without cables | Direct power delivery via cable |
| Convenience | Easy placement, no plug-in needed | Requires plugging and unplugging |
| Charge Speed | Slower, typically up to 15W | Faster, ranging 18W to 100W+ |
| Compatibility | Compatible with Qi-enabled devices | Works with any device with matching port |
| Portability | Less portable, requires flat surface | Highly portable with cables |
| Durability | Less wear on device ports | Wear and tear on charging ports over time |
| Price | Generally higher priced | Generally more affordable |
Introduction to Wireless and Wired Chargers
Wireless chargers use electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a charging pad and compatible devices, eliminating the need for cables and offering convenient, cable-free charging. Wired chargers deliver power through a physical connection using USB cables, providing faster and more efficient charging speeds due to direct power transfer. Both charging methods serve distinct user preferences, balancing convenience and charging performance for smartphones, tablets, and other electronic accessories.
Charging Speed: Wireless vs Wired
Wired chargers typically offer faster charging speeds, delivering up to 60W or more depending on the charger and device compatibility, enabling rapid power transfer. Wireless chargers generally provide speeds ranging from 5W to 15W, with advanced models supporting up to 30W, but still lag behind wired counterparts in efficiency. Heat generation during wireless charging can reduce performance, making wired charging the preferred choice for users prioritizing maximum charging speed.
Convenience and Usability Comparison
Wireless chargers offer enhanced convenience by eliminating the need for cables, allowing users to simply place their devices on the charging pad for seamless power replenishment. Wired chargers generally provide faster charging speeds but require physical connection, which can limit usability in busy or cluttered environments. The choice between wireless and wired chargers depends largely on prioritizing ease of use versus maximum charging efficiency.
Compatibility with Devices
Wireless chargers offer broad compatibility with devices supporting Qi wireless charging standards, enabling seamless charging for most modern smartphones, smartwatches, and earbuds. Wired chargers deliver faster and more consistent power across a wider range of devices, including those lacking wireless charging capabilities or requiring higher wattage for rapid charging. Device compatibility depends on factors such as charging port type (USB-C, Lightning, Micro USB), output power, and support for proprietary fast-charging technologies.
Portability and Design Considerations
Wireless chargers offer superior portability due to their cable-free design, enabling easy transport and use without tangled cords, making them ideal for travel and clutter-free spaces. Wired chargers, while less portable due to attached cables, typically have a slimmer profile and require fewer components, often resulting in a more compact and lightweight charger design. Design considerations for wireless chargers include surface area for induction coils and ventilation for heat dissipation, whereas wired chargers focus on connector durability and cable length customization.
Safety and Heat Management
Wireless chargers incorporate advanced safety features such as overcurrent protection, temperature regulation, and foreign object detection to minimize risks during charging. Wired chargers tend to deliver power more efficiently with less heat generation, reducing thermal stress on devices and potential hazards. Effective heat management in wireless charging relies on proper receiver alignment and quality coil design to prevent overheating and ensure safe operation.
Cost Analysis: Wireless vs Wired Chargers
Wireless chargers typically cost 20% to 40% more than wired chargers due to advanced technology and convenience features. Wired chargers offer faster charging speeds and lower initial investment, making them cost-effective for bulk purchasing. Long-term expenses also include potential cable replacements for wired chargers, whereas wireless pads incur minimal wear but higher upfront costs.
Durability and Lifespan
Wireless chargers typically have fewer physical connectors, reducing wear and tear and enhancing durability compared to wired chargers. Wired chargers often experience cable fraying and connector damage due to frequent bending and plugging, which can shorten their lifespan. High-quality wireless charging pads are designed to maintain consistent performance over years of use, making them a more durable choice for long-term device charging.
Environmental Impact of Charging Accessories
Wireless chargers generally consume more energy than wired chargers due to inefficiencies in power transfer, resulting in higher carbon emissions over time. Wired chargers offer more direct energy transmission, minimizing electricity waste and reducing environmental impact. Selecting wired charging accessories can contribute to lower overall energy consumption and a smaller carbon footprint in daily device usage.
Future Trends in Charging Technology
Wireless chargers are advancing with faster power delivery and integration of AI for optimized charging efficiency, reducing cable clutter and enhancing user convenience. Wired chargers continue to evolve through ultra-fast charging capabilities and improved USB-C standards, supporting higher wattage and faster data transfer. Emerging technologies like magnetic resonance and graphene-based materials promise to revolutionize both wireless and wired charging with greater speed and energy efficiency.
Wireless charger vs wired charger Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com