Magnetic chargers offer precise alignment and secure attachment, reducing charging interruptions for devices with compatible magnetic connectors. Qi chargers provide universal compatibility and convenience by enabling wireless charging for a wide range of devices without the need for exact positioning. Choosing between magnetic and Qi chargers depends on the priority of fast, reliable connection versus broad device support and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
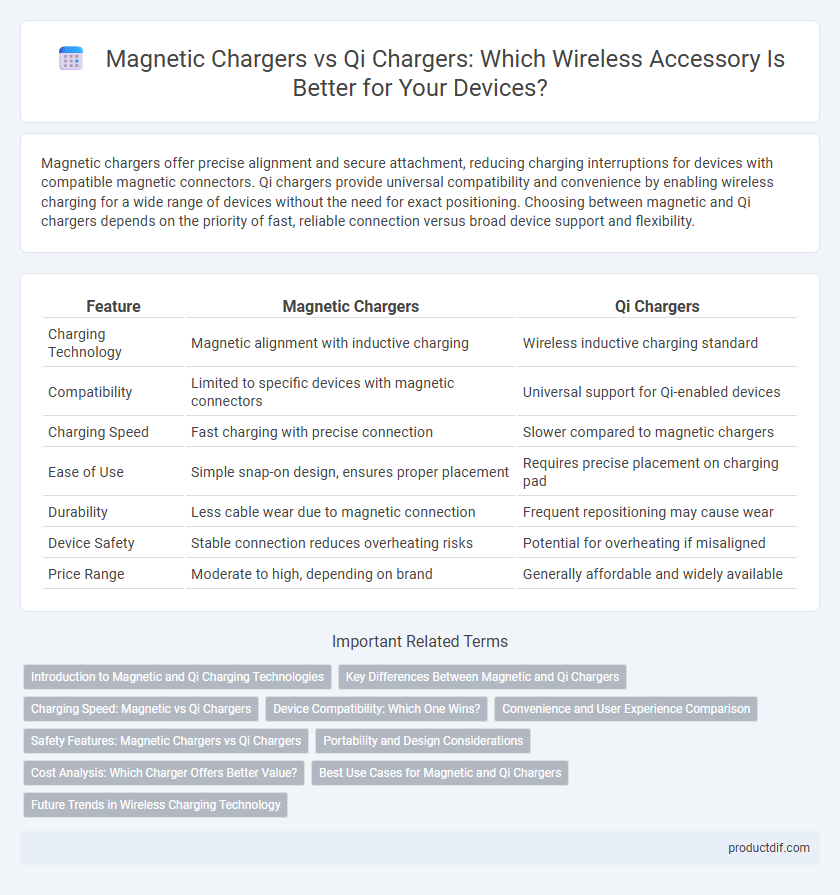
| Feature | Magnetic Chargers | Qi Chargers |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Technology | Magnetic alignment with inductive charging | Wireless inductive charging standard |
| Compatibility | Limited to specific devices with magnetic connectors | Universal support for Qi-enabled devices |
| Charging Speed | Fast charging with precise connection | Slower compared to magnetic chargers |
| Ease of Use | Simple snap-on design, ensures proper placement | Requires precise placement on charging pad |
| Durability | Less cable wear due to magnetic connection | Frequent repositioning may cause wear |
| Device Safety | Stable connection reduces overheating risks | Potential for overheating if misaligned |
| Price Range | Moderate to high, depending on brand | Generally affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Magnetic and Qi Charging Technologies
Magnetic chargers utilize magnets to align and securely connect the charging coil with the device, ensuring efficient power transfer with minimal misalignment. Qi charging technology, an established wireless power standard developed by the Wireless Power Consortium, uses electromagnetic induction to transmit electricity over short distances without physical connectors. Both technologies prioritize convenience and cable-free charging, but Qi chargers offer broader device compatibility and standardized safety protocols.
Key Differences Between Magnetic and Qi Chargers
Magnetic chargers utilize magnets to securely attach the charger to the device, ensuring precise alignment for efficient power transfer, while Qi chargers rely on wireless induction technology without physical connectors. Magnetic chargers often provide faster charging speeds due to direct contact and reduced energy loss, whereas Qi chargers offer more universal compatibility across multiple devices without the need for exact positioning. Compatibility, charging speed, and ease of alignment are the primary differences distinguishing magnetic chargers from Qi chargers in the accessory market.
Charging Speed: Magnetic vs Qi Chargers
Magnetic chargers often provide faster charging speeds due to their direct alignment and secure connection, reducing energy loss compared to standard Qi chargers. Qi chargers rely on electromagnetic induction, which can lead to slower charging rates especially if the device is misaligned or positioned incorrectly. For optimal charging speed, magnetic chargers maintain consistent power transfer, making them preferable for quick energy replenishment.
Device Compatibility: Which One Wins?
Magnetic chargers excel in compatibility with specific device models designed with built-in magnets, primarily supporting select smartphones and wearables from brands like Apple and Samsung. Qi chargers offer broader device compatibility, working with any Qi-enabled device, including smartphones, earbuds, and tablets from various manufacturers. For users seeking wide-ranging device support without brand restrictions, Qi chargers present a more versatile charging solution.
Convenience and User Experience Comparison
Magnetic chargers offer effortless alignment and stable connection, reducing charging interruptions compared to Qi chargers that require precise placement on the charging pad. The snap-on design of magnetic chargers enhances portability and ease of use, allowing seamless one-handed operation ideal for frequent device access. Qi chargers provide universal compatibility but may demand more attention to positioning, impacting overall convenience and user experience in everyday charging scenarios.
Safety Features: Magnetic Chargers vs Qi Chargers
Magnetic chargers offer enhanced safety features by ensuring a secure connection that reduces the risk of overheating and short circuits, thanks to their precise alignment and detachable design. Qi chargers incorporate foreign object detection (FOD) technology to prevent charging when metal objects are detected, minimizing fire hazards. Both charger types include over-current and over-voltage protection, but magnetic chargers provide a more stable connection that reduces wear on ports and potential electrical damage.
Portability and Design Considerations
Magnetic chargers offer superior portability with their compact, cable-free design that easily attaches to devices, reducing clutter and enhancing on-the-go convenience. Qi chargers typically require a flat surface and are bulkier due to their larger coils and charging pads, making them less portable for frequent travel. Design considerations favor magnetic chargers for sleek, integrated aesthetics and quick snap-on functionality, while Qi chargers prioritize universal compatibility across various device brands.
Cost Analysis: Which Charger Offers Better Value?
Magnetic chargers generally have higher upfront costs due to their specialized connectors and design, but they offer faster alignment and reduced wear on ports, enhancing device longevity. Qi chargers tend to be more affordable with broad compatibility across various devices, making them a cost-effective choice for users prioritizing versatility. Evaluating total value involves considering factors like charging speed, device protection, and ecosystem compatibility alongside initial price.
Best Use Cases for Magnetic and Qi Chargers
Magnetic chargers excel in scenarios requiring quick, effortless attachment and alignment, making them ideal for on-the-go charging of devices like smartwatches and wireless earbuds. Qi chargers offer broader compatibility and convenience for everyday use, supporting a wide range of smartphones and other gadgets without the need for precise positioning. Choosing between magnetic and Qi chargers depends on device type, user mobility, and preference for charging speed versus universal accessibility.
Future Trends in Wireless Charging Technology
Magnetic chargers leverage precise alignment through magnets to enhance charging efficiency, while Qi chargers rely on electromagnetic induction for widespread compatibility across devices. Future trends in wireless charging technology emphasize faster power transfer, smart device integration, and extended range capabilities, with magnetic alignment poised to reduce energy loss and improve user experience. Innovations like resonant wireless charging and integration with Internet of Things (IoT) devices will drive the evolution of both magnetic and Qi charging standards.
Magnetic chargers vs Qi chargers Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com