Electronic toys offer interactive features and sensory stimulation through lights, sounds, and movement, enhancing a child's engagement and learning experience. Manual toys promote creativity, fine motor skills, and imagination by encouraging hands-on play without reliance on batteries or technology. Both types of toys play essential roles in child development, balancing technological interaction with traditional tactile exploration.
Table of Comparison
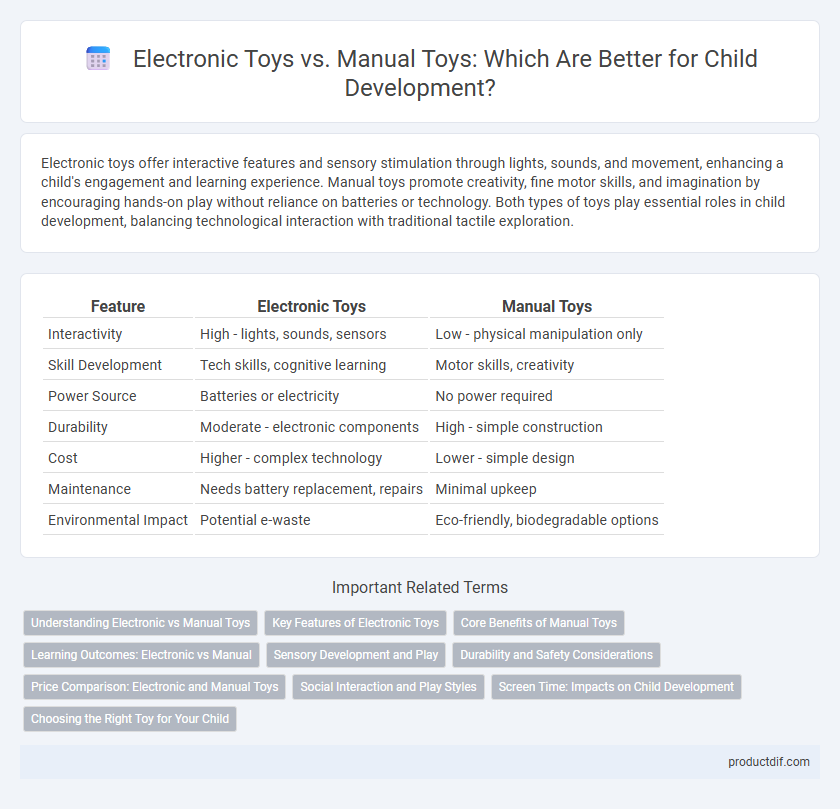
| Feature | Electronic Toys | Manual Toys |
|---|---|---|
| Interactivity | High - lights, sounds, sensors | Low - physical manipulation only |
| Skill Development | Tech skills, cognitive learning | Motor skills, creativity |
| Power Source | Batteries or electricity | No power required |
| Durability | Moderate - electronic components | High - simple construction |
| Cost | Higher - complex technology | Lower - simple design |
| Maintenance | Needs battery replacement, repairs | Minimal upkeep |
| Environmental Impact | Potential e-waste | Eco-friendly, biodegradable options |
Understanding Electronic vs Manual Toys
Electronic toys utilize batteries and integrated circuits to provide interactive features such as lights, sounds, and motion, enhancing sensory engagement and fostering cognitive development. Manual toys rely on physical manipulation, promoting fine motor skills and imaginative play through hands-on interaction without electronic components. Understanding the differences helps parents select age-appropriate toys that balance technology use with tactile learning experiences.
Key Features of Electronic Toys
Electronic toys feature interactive elements such as lights, sounds, and motion sensors that enhance sensory engagement and stimulate cognitive development. They often incorporate programmable functions and connect to apps or other devices, offering customizable play experiences and educational content. Battery-operated components and advanced technology enable dynamic responses, making electronic toys highly appealing and versatile compared to manual toys.
Core Benefits of Manual Toys
Manual toys stimulate creativity and fine motor skills by encouraging hands-on interaction without screens or batteries. They enhance cognitive development through imaginative play, problem-solving, and tactile exploration. These toys promote social bonding and physical activity, fostering essential childhood learning and growth.
Learning Outcomes: Electronic vs Manual
Electronic toys enhance learning outcomes by providing interactive features that develop cognitive skills, such as problem-solving, spatial awareness, and language acquisition through multimedia stimuli. Manual toys foster fine motor skills, creativity, and social interaction by encouraging hands-on manipulation and imaginative play without relying on digital prompts. Both types of toys contribute uniquely to child development, with electronic toys emphasizing sensory engagement and manual toys promoting physical dexterity and independent thinking.
Sensory Development and Play
Electronic toys enhance sensory development by integrating lights, sounds, and interactive features that engage auditory and visual senses more intensively. Manual toys promote tactile exploration and fine motor skills through physical manipulation, encouraging creativity and imaginative play. Combining both types supports a balanced sensory experience, fostering cognitive and sensory development in children.
Durability and Safety Considerations
Electronic toys often feature advanced safety mechanisms such as insulated wiring and low-voltage circuits, enhancing child protection against electrical hazards. Manual toys, typically constructed from robust materials like wood or durable plastics, offer greater resistance to wear and tear, ensuring longer lifespan under rough play conditions. When selecting toys, prioritizing certifications like ASTM F963 or EN71 helps ensure compliance with safety and durability standards.
Price Comparison: Electronic and Manual Toys
Electronic toys generally have higher price points due to integrated technology such as sensors, lights, and sound modules, which increase production costs. Manual toys, often made of simpler materials like wood or plastic without electronic features, tend to be more affordable and accessible. Market analysis shows electronic toys typically cost 30-50% more than their manual counterparts, reflecting their advanced functionalities and appeal.
Social Interaction and Play Styles
Electronic toys encourage interactive play through digital features and voice recognition, enhancing cooperative and competitive games among children. Manual toys, such as building blocks or dolls, promote hands-on engagement and imaginative role-playing that develop social skills by encouraging direct communication and teamwork. Both toy types offer unique benefits in fostering social interaction, with electronic toys leaning towards tech-based collaboration and manual toys supporting tactile and creative social play.
Screen Time: Impacts on Child Development
Electronic toys often contribute to increased screen time, which can impact a child's cognitive and social development by limiting physical activity and face-to-face interactions. Manual toys, like puzzles or building blocks, encourage hands-on learning, creativity, and motor skills without the risk of digital overstimulation. Balancing electronic and manual toys helps promote healthier development by combining technological engagement with active, imaginative play.
Choosing the Right Toy for Your Child
Electronic toys offer interactive features that enhance learning and engagement through sounds, lights, and digital games, which can stimulate cognitive development in children. Manual toys, such as building blocks and puzzles, promote creativity, fine motor skills, and problem-solving abilities by encouraging hands-on exploration and imagination. Selecting the right toy depends on your child's age, interests, and developmental needs, balancing technology-driven stimulation with tactile, real-world interaction.
Electronic toys vs manual toys Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com