Public APIs provide standardized access mechanisms allowing external developers to integrate and extend software functionality, promoting ecosystem growth and interoperability. Private APIs are designed for internal use, offering secure, controlled interactions within an organization's applications to enhance system stability and confidentiality. Choosing between public and private APIs depends on the desired level of access, security requirements, and development objectives.
Table of Comparison
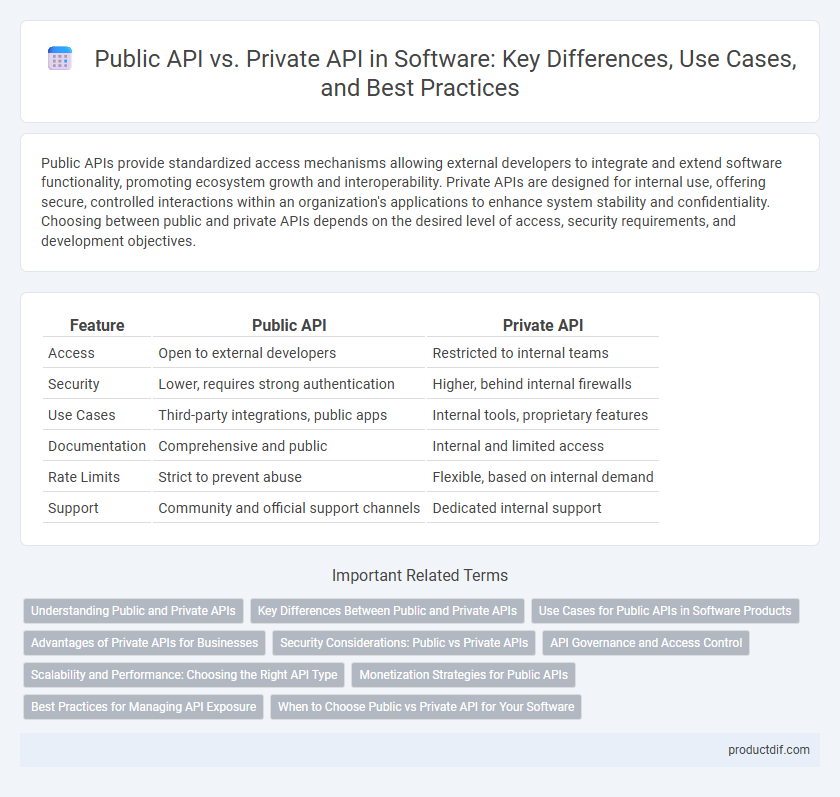
| Feature | Public API | Private API |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Open to external developers | Restricted to internal teams |
| Security | Lower, requires strong authentication | Higher, behind internal firewalls |
| Use Cases | Third-party integrations, public apps | Internal tools, proprietary features |
| Documentation | Comprehensive and public | Internal and limited access |
| Rate Limits | Strict to prevent abuse | Flexible, based on internal demand |
| Support | Community and official support channels | Dedicated internal support |
Understanding Public and Private APIs
Public APIs provide open access to external developers, enabling integration and interaction with software platforms, while private APIs are restricted for internal use within an organization to enhance security and control. Understanding the distinction between public and private APIs is crucial for designing API strategies that balance openness with protection of sensitive data. Effective API management involves evaluating access requirements, user permissions, and the scope of functionality exposed through each API type.
Key Differences Between Public and Private APIs
Public APIs are designed for external developers, offering broad accessibility and standardized endpoints to enable third-party integrations, while private APIs restrict access to internal teams, prioritizing security and control over functionality. Public APIs often emphasize comprehensive documentation, versioning, and scalability to support diverse external use cases, whereas private APIs focus on optimizing internal workflows and maintaining proprietary business logic. Data exposure and access permissions differ significantly, with public APIs exposing limited, sanitized information compared to private APIs, which handle sensitive data with strict authentication mechanisms.
Use Cases for Public APIs in Software Products
Public APIs enable developers to integrate and extend software products, facilitating third-party app development and enhancing ecosystem connectivity. They support use cases such as enabling external applications to access services, fostering innovation through open collaboration, and driving user engagement by broadening feature accessibility. Public APIs also serve as critical tools for monetization strategies by providing scalable endpoints for external partners and developers.
Advantages of Private APIs for Businesses
Private APIs offer businesses enhanced security by restricting access to trusted developers, minimizing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized use. These APIs enable more efficient internal workflows and tighter control over software development, leading to faster innovation and improved product quality. By limiting exposure, private APIs also reduce compliance risks and help maintain regulatory standards, which is crucial in industries like finance and healthcare.
Security Considerations: Public vs Private APIs
Public APIs expose endpoints to external developers, increasing the attack surface and requiring rigorous authentication, rate limiting, and monitoring to prevent unauthorized access and abuse. Private APIs restrict access to internal systems or trusted partners, reducing exposure and enabling stricter security controls like network segmentation and IP whitelisting. Implementing proper encryption, token management, and continuous auditing is crucial for both API types to safeguard sensitive data and maintain system integrity.
API Governance and Access Control
Public APIs offer broad accessibility to external developers, necessitating stringent API governance policies to monitor usage, enforce rate limits, and secure data integrity. Private APIs restrict access to internal teams or specific partners, enabling tighter access control and enhanced security protocols tailored to organizational compliance requirements. Effective API governance ensures consistent authentication, authorization, and auditing mechanisms across both public and private APIs to mitigate risks and optimize performance.
Scalability and Performance: Choosing the Right API Type
Public APIs enable broader scalability by allowing external developers to build on existing platforms, increasing user engagement and system reach, whereas private APIs offer enhanced performance optimization through controlled access and tailored resource allocation. Selecting the right API type depends on balancing the need for external integration with the requirement for system stability and response time efficiency. Companies prioritizing rapid growth and ecosystem expansion often favor public APIs, while those emphasizing high-security and performance under constrained environments typically choose private APIs.
Monetization Strategies for Public APIs
Public APIs offer robust monetization opportunities through tiered subscription plans, usage-based billing, and developer marketplace integrations that increase accessibility and scale. Implementing rate limits and premium feature access encourages sustained revenue while maintaining performance and service quality. Strategic partnerships and analytics-driven insights further optimize API value extraction by aligning offerings with developer needs and market demand.
Best Practices for Managing API Exposure
Public APIs should follow strict versioning and authentication protocols to ensure secure access and maintain backward compatibility. Private APIs require rigorous access controls and monitoring to prevent unauthorized use and safeguard internal systems. Implementing rate limiting and detailed documentation enhances the management of API exposure, reducing security risks and improving developer experience.
When to Choose Public vs Private API for Your Software
Choosing a public API is ideal when you aim to extend your software's functionality to external developers, foster community innovation, and increase integration potential across diverse platforms. Opt for a private API when prioritizing internal use, enhanced security, and control over software interactions, ensuring sensitive data and processes remain protected. Evaluate factors such as target audience, security requirements, and scalability needs to determine the appropriate API type for your software architecture.
Public API vs Private API Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com