Backend development handles server-side logic, database interactions, and application performance, ensuring data processing and security. Frontend development focuses on user interface design, responsive layouts, and seamless user experiences through HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Both areas require distinct skill sets but collaborate closely to build efficient, scalable, and user-friendly software applications.
Table of Comparison
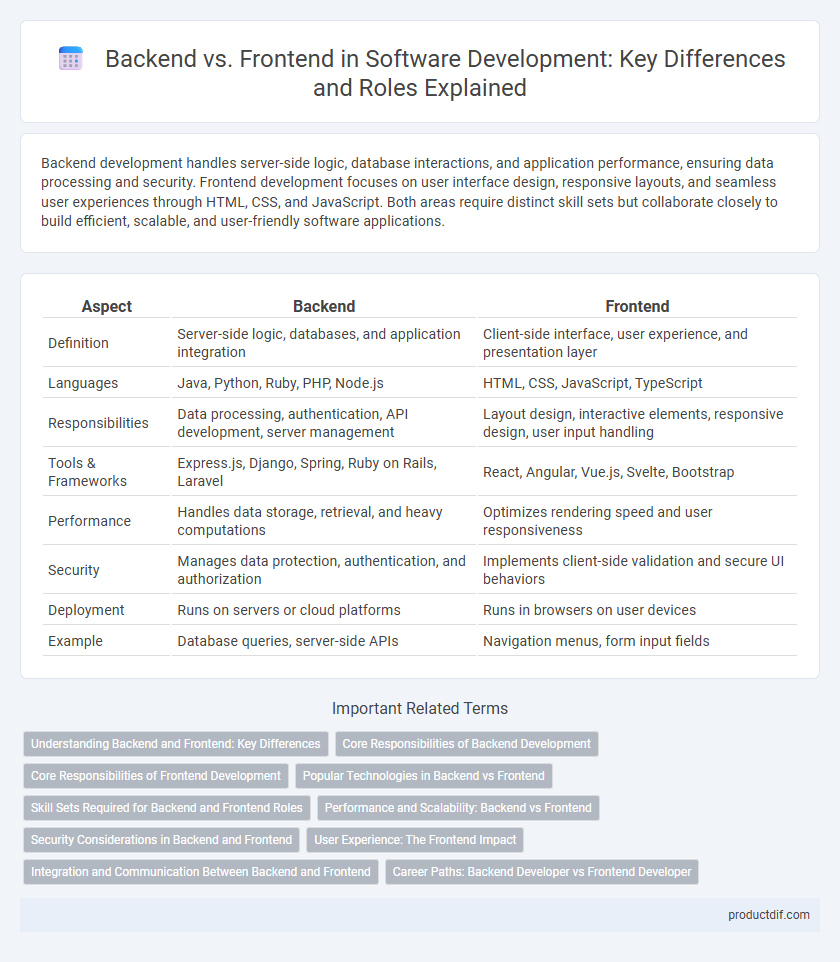
| Aspect | Backend | Frontend |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Server-side logic, databases, and application integration | Client-side interface, user experience, and presentation layer |
| Languages | Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, Node.js | HTML, CSS, JavaScript, TypeScript |
| Responsibilities | Data processing, authentication, API development, server management | Layout design, interactive elements, responsive design, user input handling |
| Tools & Frameworks | Express.js, Django, Spring, Ruby on Rails, Laravel | React, Angular, Vue.js, Svelte, Bootstrap |
| Performance | Handles data storage, retrieval, and heavy computations | Optimizes rendering speed and user responsiveness |
| Security | Manages data protection, authentication, and authorization | Implements client-side validation and secure UI behaviors |
| Deployment | Runs on servers or cloud platforms | Runs in browsers on user devices |
| Example | Database queries, server-side APIs | Navigation menus, form input fields |
Understanding Backend and Frontend: Key Differences
Backend refers to the server-side development responsible for database management, server logic, and application integration, enabling data processing and functionality behind the scenes. Frontend focuses on client-side development, involving user interface (UI) design, responsive layouts, and user experience (UX) to ensure seamless interaction and visual representation in web or mobile applications. Understanding the distinction between backend and frontend is crucial for optimizing software architecture, improving performance, and delivering comprehensive digital solutions.
Core Responsibilities of Backend Development
Backend development focuses on server-side logic, database management, and application architecture to ensure seamless data processing and storage. It involves creating APIs, handling authentication, and managing server security to support frontend functionalities. Core responsibilities also include optimizing performance and scalability to maintain robust and efficient software systems.
Core Responsibilities of Frontend Development
Frontend development focuses on designing and implementing user interfaces that ensure seamless interaction and optimal user experience across devices. Key responsibilities include translating UI/UX designs into responsive layouts using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular. Frontend developers also optimize performance, handle client-side logic, and ensure accessibility and cross-browser compatibility.
Popular Technologies in Backend vs Frontend
Popular backend technologies include Node.js, Django, Ruby on Rails, and Spring Boot, which handle server-side logic, database management, and API development. Frontend development predominantly uses React, Angular, and Vue.js for creating interactive user interfaces and enhancing user experience. Both layers rely on complementary tools like RESTful APIs and GraphQL to enable seamless communication between client and server.
Skill Sets Required for Backend and Frontend Roles
Backend development demands strong proficiency in server-side languages such as Python, Java, or Node.js, along with expertise in database management, API design, and server architecture. Frontend roles require mastery of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular, emphasizing responsive design, user experience, and client-side performance optimization. Both skill sets benefit from knowledge of version control systems, debugging tools, and collaboration platforms to ensure seamless integration and deployment.
Performance and Scalability: Backend vs Frontend
Backend performance relies heavily on server processing power, database efficiency, and optimized API design to handle large volumes of requests and data transactions. Frontend performance depends on efficient rendering, minimized resource load, and responsive user interfaces to ensure fast load times and smooth interactions. Scalability in backend involves horizontal scaling of servers and databases, while frontend scalability focuses on modular architecture and cache management to support growing user bases without degrading experience.
Security Considerations in Backend and Frontend
Backend security focuses on protecting databases, servers, and application logic by implementing strong authentication, encryption, and secure APIs to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Frontend security involves safeguarding the user interface through input validation, preventing cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, and ensuring secure session management to protect users from client-side vulnerabilities. Both layers require continuous monitoring and updates to mitigate evolving threats and maintain the overall integrity of the software system.
User Experience: The Frontend Impact
Frontend development directly shapes the user experience by designing intuitive interfaces and ensuring smooth interactions, which increases engagement and satisfaction. Responsive layouts and optimized loading speeds on the frontend reduce friction, making applications accessible across devices. While backend handles data processing and logic, the frontend's impact on usability is critical for retaining users and delivering a seamless digital experience.
Integration and Communication Between Backend and Frontend
Backend and frontend integration hinges on APIs that facilitate seamless data exchange, enabling dynamic user interfaces powered by server-side logic. RESTful services and GraphQL offer flexible communication protocols, enhancing real-time responsiveness and efficient resource management. Secure authentication methods, such as OAuth and JWT, ensure protected interactions between frontend clients and backend servers.
Career Paths: Backend Developer vs Frontend Developer
Backend developers specialize in server-side logic, database management, and application architecture, often working with languages like Python, Java, or Node.js to build scalable systems. Frontend developers focus on user interface design, user experience optimization, and client-side scripting using technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular. Career growth in backend development often leads to roles like DevOps Engineer or Software Architect, whereas frontend expertise can progress toward UX/UI Designer or Full-Stack Developer positions.
Backend vs Frontend Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com