AHA exfoliation targets the skin's surface by gently removing dead skin cells and promoting cell turnover, making it ideal for improving texture and brightening dull complexions. BHA exfoliation penetrates deeper into pores, effectively dissolving excess oil and reducing acne, making it suitable for oily and acne-prone skin. Choosing between AHA and BHA depends on individual skin concerns, with AHAs benefiting dry or sun-damaged skin and BHAs excelling in managing clogged pores and inflammation.
Table of Comparison
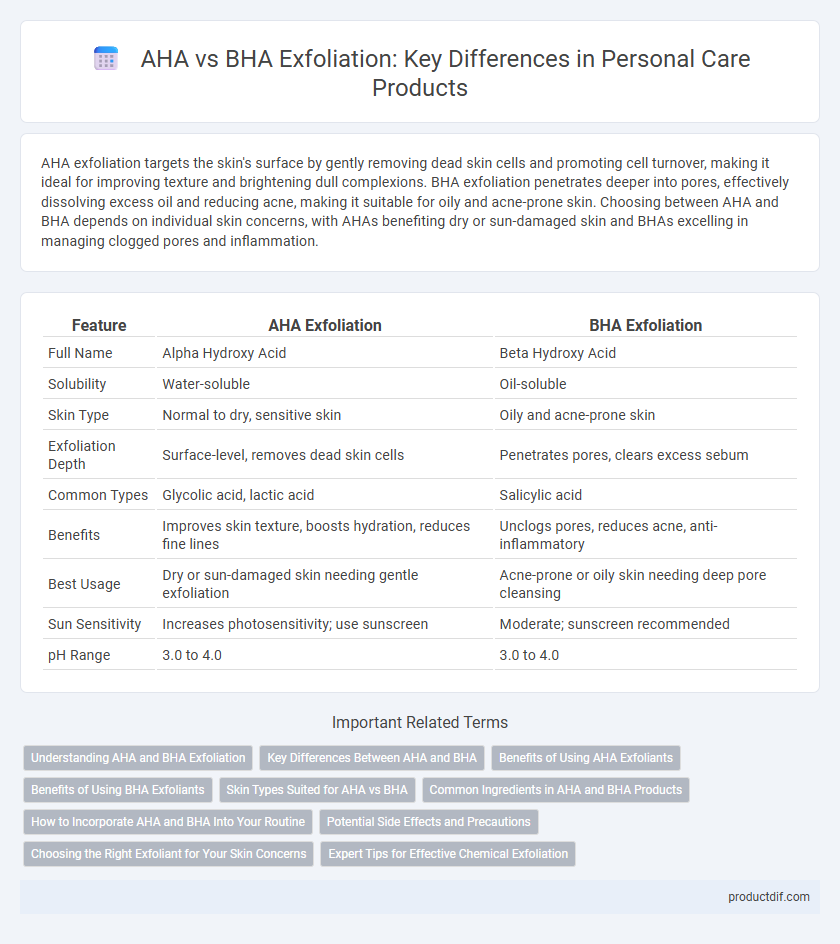
| Feature | AHA Exfoliation | BHA Exfoliation |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Alpha Hydroxy Acid | Beta Hydroxy Acid |
| Solubility | Water-soluble | Oil-soluble |
| Skin Type | Normal to dry, sensitive skin | Oily and acne-prone skin |
| Exfoliation Depth | Surface-level, removes dead skin cells | Penetrates pores, clears excess sebum |
| Common Types | Glycolic acid, lactic acid | Salicylic acid |
| Benefits | Improves skin texture, boosts hydration, reduces fine lines | Unclogs pores, reduces acne, anti-inflammatory |
| Best Usage | Dry or sun-damaged skin needing gentle exfoliation | Acne-prone or oily skin needing deep pore cleansing |
| Sun Sensitivity | Increases photosensitivity; use sunscreen | Moderate; sunscreen recommended |
| pH Range | 3.0 to 4.0 | 3.0 to 4.0 |
Understanding AHA and BHA Exfoliation
AHA exfoliation primarily targets the skin's surface by dissolving dead skin cells, making it ideal for improving texture and brightness, especially for dry or sun-damaged skin. BHA exfoliation, with salicylic acid as its key component, penetrates deeper into pores to effectively reduce oil and acne, making it suitable for oily and acne-prone skin types. Understanding the distinct properties of AHA and BHA exfoliants helps in selecting the right product for specific skin concerns and maintaining a balanced skincare routine.
Key Differences Between AHA and BHA
AHA exfoliants, derived primarily from natural acids like glycolic and lactic acid, primarily target the skin's surface by breaking down dead skin cells and enhancing hydration, making them ideal for dry and sun-damaged skin. BHA exfoliants, such as salicylic acid, penetrate deeper into pores to effectively dissolve excess oil and unclog follicles, which helps prevent acne and is well-suited for oily and acne-prone skin types. The choice between AHA and BHA depends on skin concerns: AHAs improve texture and brighten complexion, while BHAs reduce inflammation and control sebum production.
Benefits of Using AHA Exfoliants
AHA exfoliants, derived from natural fruit acids like glycolic and lactic acid, effectively remove dead skin cells on the surface, promoting smoother texture and brighter complexion. Their water-soluble nature makes them ideal for dry and sun-damaged skin, enhancing hydration and collagen production. Regular use of AHAs can reduce fine lines, improve skin tone, and accelerate cellular turnover for a youthful glow.
Benefits of Using BHA Exfoliants
BHA exfoliants, such as salicylic acid, effectively penetrate and clear clogged pores, making them ideal for acne-prone and oily skin types. They reduce inflammation, minimize blackheads, and promote smoother skin texture by removing dead skin cells from inside the pores. Regular use of BHA exfoliants can also improve overall complexion clarity and prevent future breakouts.
Skin Types Suited for AHA vs BHA
AHA exfoliation is ideal for dry or sun-damaged skin due to its ability to gently remove surface dead cells and improve hydration. BHA exfoliation suits oily and acne-prone skin because it penetrates pores, dissolving excess sebum and reducing inflammation. Choosing between AHA and BHA depends on skin type, sensitivity, and specific skin concerns for optimal results.
Common Ingredients in AHA and BHA Products
Common ingredients in AHA exfoliation products include glycolic acid, lactic acid, and mandelic acid, which are derived from natural sources like sugar cane, milk, and almonds. BHA exfoliants primarily feature salicylic acid, known for its oil-soluble properties that penetrate deep into pores to clear excess sebum and impurities. Both AHAs and BHAs target skin renewal but differ in molecular structure and lipid affinity, making ingredient choice crucial for addressing specific skin concerns.
How to Incorporate AHA and BHA Into Your Routine
Incorporate AHA exfoliation, like glycolic or lactic acid, into your evening skincare routine to promote surface cell turnover and improve skin texture. Use BHA exfoliation, such as salicylic acid, in the morning to penetrate pores, reduce blackheads, and control oil production. Start with low concentrations of each acid, applying them on alternate days to minimize irritation, and always follow with broad-spectrum sunscreen to protect sensitive, exfoliated skin.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
AHA exfoliation may cause increased skin sensitivity, redness, and irritation, particularly for those with dry or sensitive skin, due to its water-soluble nature targeting the skin's surface. BHA exfoliation, often salicylic acid-based, penetrates oily pores and can lead to dryness, peeling, or mild stinging, especially if overused or combined with other harsh treatments. It is crucial to apply sunscreen daily after using either AHA or BHA exfoliants to prevent photosensitivity and consult with a dermatologist to tailor usage according to skin type and condition.
Choosing the Right Exfoliant for Your Skin Concerns
AHA exfoliants, derived from natural fruit acids, effectively target surface-level concerns such as dullness, uneven texture, and fine lines by promoting gentle skin cell turnover. BHA exfoliants, primarily salicylic acid, penetrate deeper into pores to combat acne, blackheads, and excess sebum, making them ideal for oily and acne-prone skin types. Selecting the appropriate exfoliant depends on your skin concerns: choose AHAs for brightening and anti-aging benefits, while BHAs are best for reducing inflammation and unclogging pores.
Expert Tips for Effective Chemical Exfoliation
Effective chemical exfoliation requires understanding the distinct benefits of AHA and BHA acids; AHAs like glycolic acid target surface dead skin cells for smoother texture, while BHAs such as salicylic acid penetrate pores to reduce acne and excess oil. Experts recommend starting with lower concentrations of AHAs and BHAs to assess skin tolerance and gradually increasing use to avoid irritation. Consistent application combined with daily sunscreen enhances exfoliation results and protects newly revealed skin from UV damage.
AHA exfoliation vs BHA exfoliation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com