Map navigation offers a reliable, battery-free option for outdoor gear pet owners, allowing them to track trails and landmarks without signal dependence. GPS navigation provides real-time location tracking and route updates, enhancing safety and convenience during outdoor adventures. Combining both methods ensures preparedness in diverse terrains and conditions.
Table of Comparison
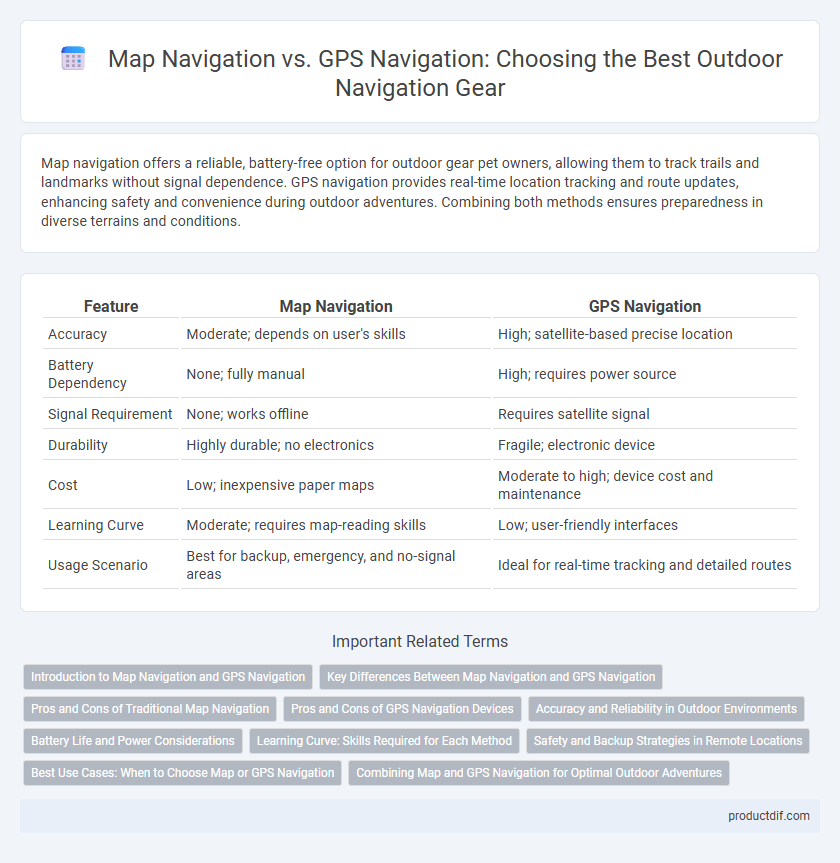
| Feature | Map Navigation | GPS Navigation |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Moderate; depends on user's skills | High; satellite-based precise location |
| Battery Dependency | None; fully manual | High; requires power source |
| Signal Requirement | None; works offline | Requires satellite signal |
| Durability | Highly durable; no electronics | Fragile; electronic device |
| Cost | Low; inexpensive paper maps | Moderate to high; device cost and maintenance |
| Learning Curve | Moderate; requires map-reading skills | Low; user-friendly interfaces |
| Usage Scenario | Best for backup, emergency, and no-signal areas | Ideal for real-time tracking and detailed routes |
Introduction to Map Navigation and GPS Navigation
Map navigation relies on reading topographic features, contour lines, and landmarks to interpret terrain and plot routes manually, offering reliability without electronic dependence. GPS navigation uses satellite signals to provide real-time positioning, route tracking, and turn-by-turn directions, enhancing precision and convenience in outdoor adventures. Understanding the strengths and limitations of both methods is essential for effective route planning and safety in wilderness exploration.
Key Differences Between Map Navigation and GPS Navigation
Map navigation relies on physical maps and compass skills, offering a tactile understanding of terrain, while GPS navigation uses satellite signals to provide real-time, precise location tracking. Map navigation requires interpreting topographic features and planning routes manually, which enhances spatial awareness but demands more skill and preparation. GPS navigation simplifies wayfinding with automated directions and updates but depends on battery life and signal availability, making it less reliable in remote or heavily forested areas.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Map Navigation
Traditional map navigation offers reliability without dependency on batteries or electronic signals, making it essential in remote outdoor environments where GPS signals may be weak or unavailable. It enhances spatial awareness and map-reading skills, providing a comprehensive understanding of terrain, which electronic devices may oversimplify. However, its effectiveness requires practice and strong interpretation skills, and it lacks real-time positioning updates, making timely route adjustments more challenging compared to GPS navigation.
Pros and Cons of GPS Navigation Devices
GPS navigation devices offer precise location tracking and real-time route guidance, essential for hiking and remote outdoor adventures where traditional maps may be difficult to interpret. They provide features such as waypoints, distance measurement, and emergency SOS signals, enhancing safety and convenience for outdoor enthusiasts. However, GPS devices rely on battery power and satellite signals, which can fail in dense forests or deep canyons, and they may lack the broader spatial context that physical maps provide.
Accuracy and Reliability in Outdoor Environments
Map navigation offers reliable accuracy by providing a constant reference that is unaffected by battery life or signal loss, essential in dense forests or remote mountain areas where GPS signals often falter. GPS navigation excels in pinpoint accuracy under open skies with real-time location tracking and route updates, crucial for dynamic or unfamiliar terrain. Combining traditional map skills with GPS technology ensures enhanced navigational precision and dependable guidance in varied outdoor environments.
Battery Life and Power Considerations
Map navigation requires no battery power, making it ideal for extended outdoor trips where conserving energy is crucial, while GPS navigation depends heavily on battery life and can drain power quickly, especially with continuous use and high screen brightness. Portable power banks and solar chargers are essential accessories for GPS devices to ensure uninterrupted navigation. Choosing between maps and GPS involves balancing reliability and power availability against real-time location tracking and ease of use.
Learning Curve: Skills Required for Each Method
Map navigation demands proficiency in reading topographic features, understanding symbols, and using a compass for accurate orientation, making it essential for outdoor enthusiasts to develop spatial awareness and problem-solving skills. GPS navigation simplifies route tracking by providing real-time location data and turn-by-turn directions, but reliance on technology can reduce the development of natural navigation instincts. Mastering map skills offers a foundational benefit for backup navigation, while GPS provides convenience and precision in complex terrains.
Safety and Backup Strategies in Remote Locations
Map navigation offers a reliable safety backup in remote locations where GPS signals may be weak or unavailable due to dense foliage or rugged terrain. Experienced outdoor enthusiasts carry both a detailed topographic map and a compass as essential backup tools to prevent reliance on potentially failing GPS devices. Combining GPS navigation with traditional map skills enhances situational awareness and ensures safer route planning and emergency preparedness in wilderness environments.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose Map or GPS Navigation
Map navigation excels in remote areas with limited signal, offering reliable orientation through physical landmarks and topographic details. GPS navigation is ideal for urban environments or unfamiliar terrain, providing real-time location tracking and route recalculations using satellite data. Combining both methods ensures safety and accuracy in diverse outdoor adventures.
Combining Map and GPS Navigation for Optimal Outdoor Adventures
Using both map navigation and GPS navigation enhances outdoor adventures by providing reliable backup and greater situational awareness. Topographic maps offer detailed terrain understanding while GPS devices supply real-time location tracking and route data. Combining these tools ensures accuracy and safety, especially in remote areas where GPS signals may falter.
Map navigation vs GPS navigation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com