Low-voltage lighting fixtures operate at 12 volts and provide enhanced safety and energy efficiency, ideal for accent or landscape lighting. Line-voltage fixtures run at the standard 120 volts, delivering higher power suitable for general indoor and outdoor illumination. Choosing between low-voltage and line-voltage fixtures depends on the specific lighting needs, installation complexity, and desired ambiance for pet-safe environments.
Table of Comparison
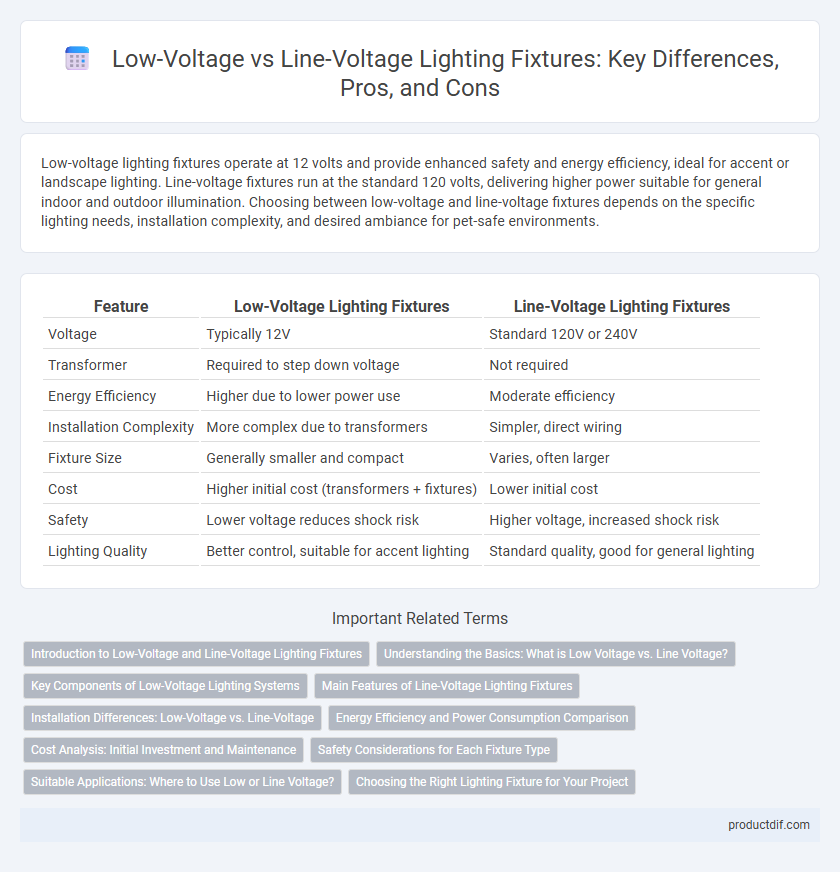
| Feature | Low-Voltage Lighting Fixtures | Line-Voltage Lighting Fixtures |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Typically 12V | Standard 120V or 240V |
| Transformer | Required to step down voltage | Not required |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher due to lower power use | Moderate efficiency |
| Installation Complexity | More complex due to transformers | Simpler, direct wiring |
| Fixture Size | Generally smaller and compact | Varies, often larger |
| Cost | Higher initial cost (transformers + fixtures) | Lower initial cost |
| Safety | Lower voltage reduces shock risk | Higher voltage, increased shock risk |
| Lighting Quality | Better control, suitable for accent lighting | Standard quality, good for general lighting |
Introduction to Low-Voltage and Line-Voltage Lighting Fixtures
Low-voltage lighting fixtures operate at 12 volts, offering enhanced energy efficiency and increased safety compared to standard line-voltage fixtures that run on 120 volts. These fixtures are commonly used in landscape lighting, under-cabinet lights, and accent lighting due to their lower heat output and compatibility with transformer systems. Line-voltage fixtures provide direct power connections, making them ideal for general illumination in residential and commercial settings where higher wattage and simpler installation are required.
Understanding the Basics: What is Low Voltage vs. Line Voltage?
Low-voltage lighting fixtures operate on 12 or 24 volts, typically requiring a transformer to step down the standard 120-volt line voltage, offering enhanced safety and energy efficiency for residential and landscape lighting. Line-voltage fixtures connect directly to the main power supply at 120 volts, providing stronger illumination and compatibility with a wider range of bulbs but with increased electrical risks and higher installation complexity. Choosing between low-voltage and line-voltage fixtures depends on factors such as installation location, desired brightness, energy consumption, and overall system safety requirements.
Key Components of Low-Voltage Lighting Systems
Low-voltage lighting systems rely on key components such as a transformer, low-voltage bulbs, and specialized wiring designed to handle reduced electrical currents. The transformer plays a critical role by stepping down standard line voltage (120V or 240V) to a safer, lower voltage, typically 12V or 24V, which enhances durability and energy efficiency. These systems often include low-voltage cables and connectors optimized for minimal voltage drop, ensuring consistent illumination and longer fixture lifespan.
Main Features of Line-Voltage Lighting Fixtures
Line-voltage lighting fixtures operate directly on standard electrical supply, typically 120 volts in the U.S., enabling compatibility with most residential and commercial wiring systems. These fixtures provide higher wattage capacity, resulting in brighter illumination suitable for large spaces and outdoor applications. Durable construction and simpler installation make line-voltage fixtures ideal for robust, long-term lighting solutions where consistent power delivery is essential.
Installation Differences: Low-Voltage vs. Line-Voltage
Low-voltage fixtures typically require a transformer to step down the voltage from 120V line-voltage to 12V or 24V, necessitating careful placement and wiring for safety and efficiency. Line-voltage fixtures connect directly to the standard 120V electrical system, often simplifying installation but requiring compliance with specific local electrical codes. Understanding these installation differences is crucial for ensuring compatibility with existing wiring infrastructure and optimizing both performance and safety in residential or commercial lighting projects.
Energy Efficiency and Power Consumption Comparison
Low-voltage lighting fixtures typically operate at 12 volts and are more energy-efficient due to reduced power loss over short distances, making them ideal for accent and landscape lighting. Line-voltage fixtures run directly on standard household voltage, generally 120 volts, and while easier to install, they consume more power and generate more heat, leading to higher energy consumption. Choosing low-voltage systems can result in significant energy savings and lower electricity bills, especially in applications requiring prolonged lighting use.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Low-voltage lighting fixtures generally have a higher initial investment due to transformers and specialized bulbs but offer reduced energy consumption and longer bulb lifespan, lowering long-term costs. Line-voltage fixtures typically feature lower upfront expenses and simpler installation but incur higher energy costs and more frequent maintenance. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals low-voltage systems save money over time despite steeper upfront investments.
Safety Considerations for Each Fixture Type
Low-voltage lighting fixtures operate at 12V or 24V, significantly reducing the risk of electrical shock and making them safer for residential and outdoor installations. Line-voltage fixtures run directly on standard building voltage (120V or 240V), which demands stricter adherence to electrical codes and professional installation to prevent hazards such as electrical shock and fire. Proper insulation, grounding, and the use of certified components are critical safety measures for both fixture types to ensure reliable and secure operation.
Suitable Applications: Where to Use Low or Line Voltage?
Low-voltage lighting fixtures, typically operating at 12 volts, are ideal for landscape lighting, under-cabinet illumination, and accent lighting due to their energy efficiency and enhanced safety in damp or outdoor environments. Line-voltage fixtures, running at standard 120 volts, are best suited for general indoor lighting applications, such as ceiling lights and wall sconces, where higher brightness and easier installation without transformers are needed. Choosing between low-voltage and line-voltage fixtures depends on the specific lighting requirements, location, and energy considerations of the project.
Choosing the Right Lighting Fixture for Your Project
Low-voltage lighting fixtures operate at 12 volts and offer enhanced energy efficiency, safety, and precise control, making them ideal for landscape and accent lighting projects. Line-voltage fixtures run directly on standard household current (120 volts), provide brighter illumination, and are suitable for general indoor and outdoor lighting where higher brightness is essential. Selecting the right lighting fixture depends on your project's voltage requirements, energy consumption goals, and desired lighting intensity.
Low-voltage fixtures vs Line-voltage fixtures Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com