Incandescent bulbs produce a warm, soft light with lower energy efficiency and shorter lifespan compared to halogen bulbs, which offer brighter, whiter light and improved energy savings. Halogen bulbs operate by using a halogen gas to increase brightness and longevity, making them a popular choice for task lighting and outdoor fixtures. Choosing between incandescent and halogen depends on balancing desired light quality, energy consumption, and fixture compatibility.
Table of Comparison
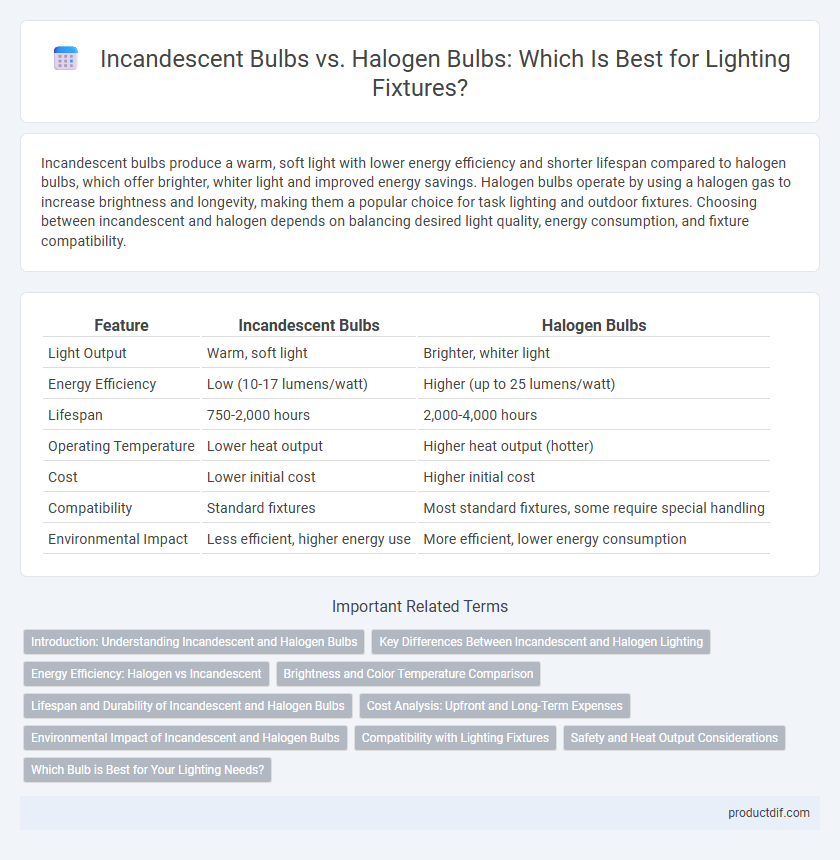
| Feature | Incandescent Bulbs | Halogen Bulbs |
|---|---|---|
| Light Output | Warm, soft light | Brighter, whiter light |
| Energy Efficiency | Low (10-17 lumens/watt) | Higher (up to 25 lumens/watt) |
| Lifespan | 750-2,000 hours | 2,000-4,000 hours |
| Operating Temperature | Lower heat output | Higher heat output (hotter) |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Compatibility | Standard fixtures | Most standard fixtures, some require special handling |
| Environmental Impact | Less efficient, higher energy use | More efficient, lower energy consumption |
Introduction: Understanding Incandescent and Halogen Bulbs
Incandescent bulbs produce light by heating a tungsten filament until it glows, offering warm, natural illumination but lower energy efficiency. Halogen bulbs improve on this design by using a halogen gas to increase lifespan and brightness while maintaining color quality. Understanding the differences in operation and performance helps in choosing the right lighting fixture for specific needs.
Key Differences Between Incandescent and Halogen Lighting
Incandescent bulbs produce light by heating a tungsten filament, resulting in lower energy efficiency and shorter lifespan compared to halogen bulbs, which use a halogen gas to increase brightness and longevity. Halogen lighting offers higher color temperature and improved light clarity, making it suitable for tasks requiring precise illumination. Energy consumption and heat output are notably lower in halogen bulbs, contributing to their growing preference in residential and commercial lighting applications.
Energy Efficiency: Halogen vs Incandescent
Halogen bulbs consume approximately 20-30% less energy compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, resulting in lower electricity bills and reduced environmental impact. The enhanced efficiency of halogen bulbs stems from their unique design that recycles heat to produce brighter light with less wasted energy. Despite a higher initial cost, halogen bulbs offer longer lifespans and improved energy savings, making them a more economical choice over time than incandescent bulbs.
Brightness and Color Temperature Comparison
Incandescent bulbs typically produce a warm yellowish light with a color temperature around 2700K, while halogen bulbs offer brighter illumination with a higher color temperature ranging from 3000K to 3200K, resulting in a whiter and more vibrant light. Halogen bulbs deliver about 20-30% more brightness than incandescent bulbs of the same wattage, enhancing visibility and detail in indoor lighting applications. The improved brightness and cooler color temperature of halogen bulbs make them a preferred choice for task lighting and areas requiring more accurate color rendering.
Lifespan and Durability of Incandescent and Halogen Bulbs
Incandescent bulbs typically have a lifespan of around 1,000 hours, whereas halogen bulbs last significantly longer, averaging between 2,000 to 4,000 hours. The durability of halogen bulbs is enhanced by their quartz envelope, which withstands higher temperatures and reduces blackening compared to the softer glass of incandescent bulbs. This increased lifespan and robust construction make halogen bulbs a more reliable option for long-term lighting needs.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Incandescent bulbs have a lower upfront cost, typically priced between $0.50 to $2 per bulb, but their lifespan of about 1,000 hours results in higher long-term replacement expenses. Halogen bulbs, priced around $1 to $5 per bulb, offer a longer lifespan of 2,000 to 4,000 hours and greater energy efficiency, reducing overall electricity costs. When factoring in both purchase price and energy consumption, halogen bulbs tend to provide better value and lower total cost of ownership over time.
Environmental Impact of Incandescent and Halogen Bulbs
Incandescent bulbs consume significantly more energy, resulting in higher carbon emissions compared to halogen bulbs, which are more energy-efficient but still less eco-friendly than LED alternatives. Both types generate excessive heat, increasing environmental strain through wasted electricity and shorter lifespan leading to more frequent replacements. Disposal of incandescent and halogen bulbs poses environmental risks due to materials that do not decompose easily, requiring proper recycling to mitigate landfill impact.
Compatibility with Lighting Fixtures
Incandescent bulbs are widely compatible with most standard lighting fixtures due to their traditional size and base types such as E26 and E27. Halogen bulbs, while similar in shape and base, often require fixtures rated to handle higher heat output and may need specific dimmers designed for halogen technology. Ensuring fixture compatibility with wattage limits and heat tolerance is crucial when choosing between incandescent and halogen bulbs to avoid damage or safety hazards.
Safety and Heat Output Considerations
Incandescent bulbs typically generate higher heat levels, increasing the risk of burns or fire hazards, while halogen bulbs operate at higher temperatures but are designed with quartz envelopes to better withstand heat. Halogen bulbs offer improved safety due to their more efficient energy use and longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and handling. Proper fixture compatibility and ventilation are essential for both bulb types to mitigate overheating and ensure safe operation.
Which Bulb is Best for Your Lighting Needs?
Incandescent bulbs offer warm, natural light but consume more energy and have shorter lifespans compared to halogen bulbs, which produce brighter, more efficient illumination with improved color rendering. Halogen bulbs operate at higher temperatures, resulting in increased brightness and durability, making them ideal for task lighting and areas requiring focused light. Choosing between the two depends on your priorities for energy efficiency, brightness, and application-specific lighting quality.
Incandescent Bulbs vs Halogen Bulbs Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com