Ethically sourced jewelry prioritizes fair labor practices, environmental sustainability, and transparent supply chains to minimize negative impacts on workers and ecosystems. Conventional sourcing often overlooks these factors, leading to potential exploitation and environmental degradation. Choosing ethically sourced jewelry supports responsible mining and craftsmanship, promoting a more sustainable and conscientious industry.
Table of Comparison
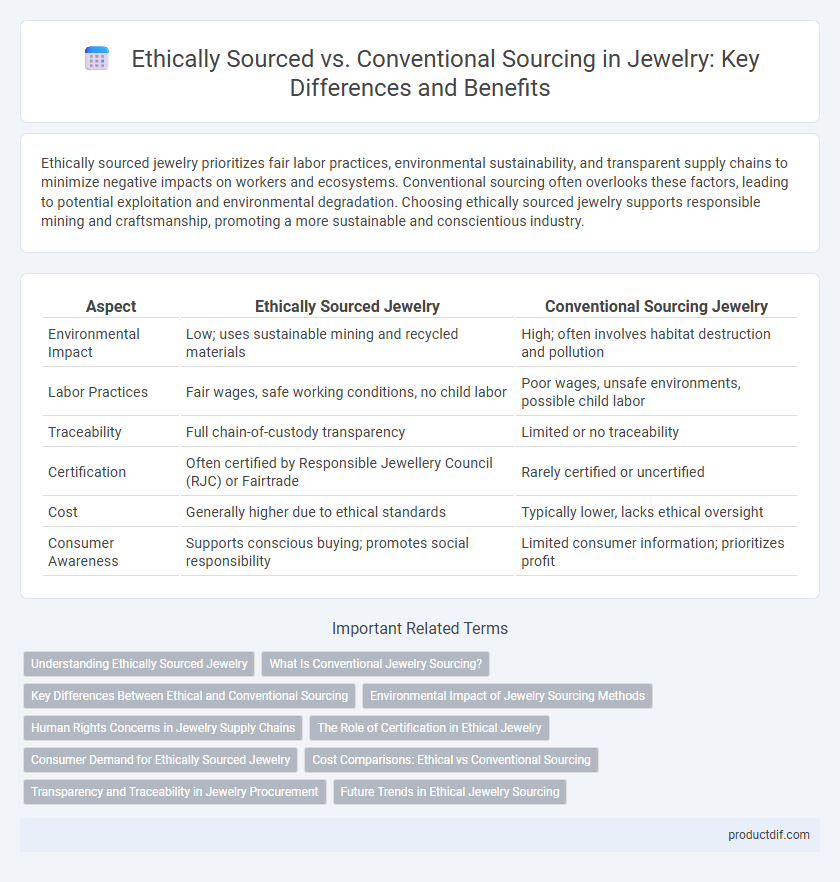
| Aspect | Ethically Sourced Jewelry | Conventional Sourcing Jewelry |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Low; uses sustainable mining and recycled materials | High; often involves habitat destruction and pollution |
| Labor Practices | Fair wages, safe working conditions, no child labor | Poor wages, unsafe environments, possible child labor |
| Traceability | Full chain-of-custody transparency | Limited or no traceability |
| Certification | Often certified by Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC) or Fairtrade | Rarely certified or uncertified |
| Cost | Generally higher due to ethical standards | Typically lower, lacks ethical oversight |
| Consumer Awareness | Supports conscious buying; promotes social responsibility | Limited consumer information; prioritizes profit |
Understanding Ethically Sourced Jewelry
Ethically sourced jewelry prioritizes transparency, fair labor practices, and environmentally sustainable mining methods, ensuring that gemstones and metals are obtained without exploitation or environmental harm. This contrasts with conventional sourcing, where supply chains often lack oversight, potentially involving conflict minerals and unsafe working conditions. Consumers seeking ethically sourced jewelry support initiatives such as Fairtrade certifications and traceable provenance to promote responsible industry standards.
What Is Conventional Jewelry Sourcing?
Conventional jewelry sourcing involves procuring gemstones and metals through traditional mining methods that often prioritize cost and volume over environmental and social impacts. This process can lead to issues such as habitat destruction, labor exploitation, and lack of transparency in supply chains. Understanding conventional sourcing highlights the importance of ethical alternatives that promote sustainability and fair labor practices.
Key Differences Between Ethical and Conventional Sourcing
Ethically sourced jewelry emphasizes transparency, environmental sustainability, and fair labor practices, ensuring materials are mined and produced without exploiting workers or harming ecosystems. Conventional sourcing often prioritizes cost-efficiency and mass production, which can lead to environmental degradation and unethical labor conditions. Key differences include the traceability of materials, adherence to strict labor standards, and commitment to reducing the carbon footprint in the ethical sourcing model.
Environmental Impact of Jewelry Sourcing Methods
Ethically sourced jewelry prioritizes sustainable mining practices that minimize habitat destruction, reduce carbon emissions, and avoid toxic chemical use, contrasting sharply with conventional sourcing methods that frequently contribute to soil erosion, water pollution, and biodiversity loss. The environmental impact of ethical sourcing is significantly lower due to stringent certifications like Fairmined and Responsible Jewellery Council, which enforce eco-friendly extraction and fair labor conditions. Conventional sources often ignore these standards, leading to higher ecological degradation and increased greenhouse gas footprints in the jewelry supply chain.
Human Rights Concerns in Jewelry Supply Chains
Ethically sourced jewelry emphasizes stringent human rights protections, ensuring miners and artisans work in safe conditions free from exploitation and child labor. Conventional sourcing often lacks transparency, increasing risks of labor abuses and unsafe practices throughout the supply chain. Supporting ethical sourcing promotes fair wages, community well-being, and responsible mining practices.
The Role of Certification in Ethical Jewelry
Certification in ethical jewelry plays a crucial role in ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain, distinguishing ethically sourced materials from conventional sourcing methods often linked to environmental damage and exploitative labor practices. Certifications such as Fairtrade, Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC), and Kimberley Process guarantee that metals and gemstones meet rigorous standards for sustainability, human rights, and conflict-free origins. These verifiable credentials empower consumers to make informed decisions and support brands committed to ethical practices in the jewelry industry.
Consumer Demand for Ethically Sourced Jewelry
Consumer demand for ethically sourced jewelry has surged as buyers prioritize transparency, environmental sustainability, and fair labor practices in the supply chain. Ethical sourcing ensures gemstones and metals are obtained without harm to communities or ecosystems, appealing to socially conscious consumers. This shift influences jewelry brands to adopt responsible sourcing standards, reshaping industry practices and market offerings.
Cost Comparisons: Ethical vs Conventional Sourcing
Ethically sourced jewelry often comes at a higher price due to fair labor practices, sustainable mining methods, and certification processes that increase production costs compared to conventional sourcing. Conventional sourcing relies on established supply chains with fewer regulations, enabling lower prices but frequently at the expense of environmental degradation and labor exploitation. Consumers opting for ethically sourced pieces invest in transparency and responsibility, which may reflect in premium prices but contribute to long-term sustainability and social impact.
Transparency and Traceability in Jewelry Procurement
Ethically sourced jewelry prioritizes transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain, ensuring that metals and gemstones are mined and processed under fair labor conditions and minimal environmental impact. Conventional sourcing often lacks detailed documentation, making it difficult to verify the origins, leading to potential conflicts and unethical practices. Leveraging blockchain and certification systems, ethically sourced jewelry provides consumers with verifiable provenance, fostering trust and accountability in jewelry procurement.
Future Trends in Ethical Jewelry Sourcing
Future trends in ethical jewelry sourcing emphasize transparency through blockchain technology, enabling consumers to trace gemstones and metals from mine to market. Sustainable mining practices and fair labor certifications are gaining wider adoption, promoting environmental stewardship and social responsibility. Consumer demand increasingly favors brands committed to cruelty-free, conflict-free, and recycled materials, driving innovation in lab-grown diamonds and recycled precious metals.
Ethically Sourced vs Conventional Sourcing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com