Engineered wood offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to warping compared to particle board, making it ideal for high-quality furniture. Particle board, while more affordable and lightweight, tends to be less durable and prone to damage from moisture and heavy use. Choosing engineered wood ensures longer-lasting furniture that maintains its structural integrity over time.
Table of Comparison
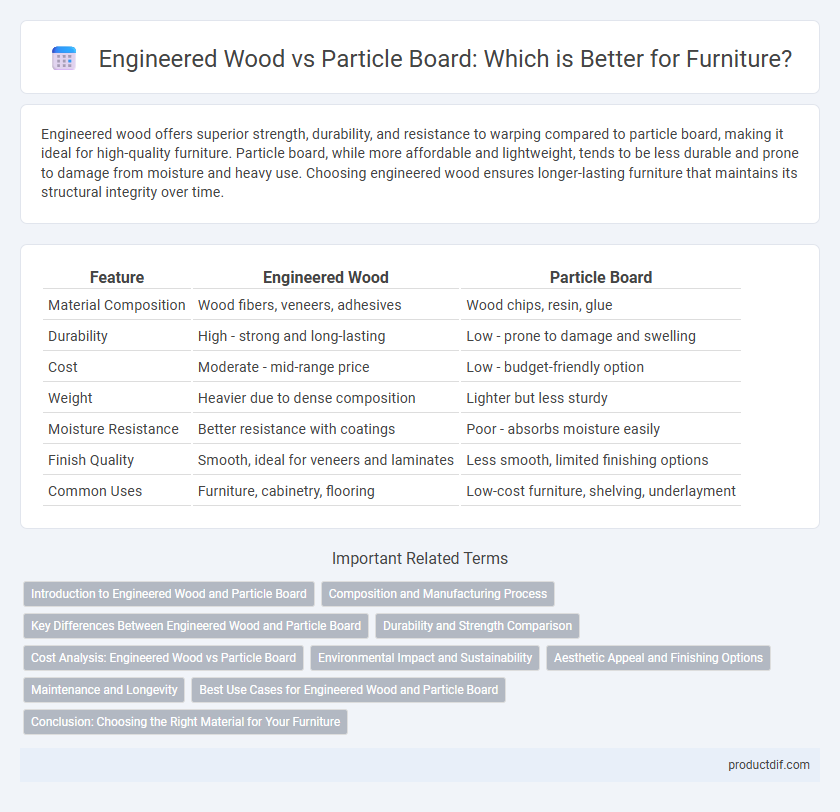
| Feature | Engineered Wood | Particle Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fibers, veneers, adhesives | Wood chips, resin, glue |
| Durability | High - strong and long-lasting | Low - prone to damage and swelling |
| Cost | Moderate - mid-range price | Low - budget-friendly option |
| Weight | Heavier due to dense composition | Lighter but less sturdy |
| Moisture Resistance | Better resistance with coatings | Poor - absorbs moisture easily |
| Finish Quality | Smooth, ideal for veneers and laminates | Less smooth, limited finishing options |
| Common Uses | Furniture, cabinetry, flooring | Low-cost furniture, shelving, underlayment |
Introduction to Engineered Wood and Particle Board
Engineered wood is a composite material made by binding wood fibers, strands, or veneers with adhesives under heat and pressure to create strong, durable panels used in furniture manufacturing. Particle board consists of wood particles, such as sawdust and chips, combined with resin and compressed into sheets, offering an economical but less robust alternative to engineered wood. Both materials serve distinct purposes in furniture production, balancing cost, strength, and appearance.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Engineered wood consists of multiple layers of wood veneers or fibers bonded together with adhesives, offering enhanced strength and stability compared to particle board, which is made from wood chips, sawdust, and resin compressed under heat and pressure. The manufacturing process of engineered wood involves precise layering and hot-pressing techniques, resulting in uniform density and resistance to warping. In contrast, particle board's composition of smaller wood particles and resin leads to a more porous structure, making it less durable and more prone to moisture damage.
Key Differences Between Engineered Wood and Particle Board
Engineered wood consists of multiple layers of wood veneer or fibers bonded together for enhanced strength and stability, whereas particle board is made from wood chips, sawmill shavings, and resin compressed into sheets. Engineered wood offers higher durability, better moisture resistance, and improved structural integrity compared to particle board, which tends to be more affordable but susceptible to damage and swelling over time. These key differences influence their suitability for various furniture applications, with engineered wood preferred for load-bearing or high-use pieces and particle board often used for budget-friendly, lightweight furniture.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Engineered wood offers superior durability and strength compared to particle board due to its layered construction with bonded wood fibers or veneers, providing enhanced resistance to warping and impact. Particle board, composed mainly of wood chips and resin, tends to be less dense and more prone to damage under heavy loads or moisture exposure. Consequently, engineered wood is preferred for high-stress furniture applications requiring long-term stability and load-bearing capacity.
Cost Analysis: Engineered Wood vs Particle Board
Engineered wood generally costs more than particle board due to higher manufacturing standards and enhanced durability. Particle board offers a budget-friendly option but may incur additional expenses over time because of its lower resistance to moisture and wear. Evaluating initial investment against long-term performance helps determine the most cost-effective choice for furniture projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Engineered wood, made from wood fibers and adhesives, offers enhanced durability and often utilizes recycled materials, reducing the need for virgin timber and minimizing deforestation. Particle board, composed primarily of wood chips and resin, typically contains more synthetic adhesives with potential formaldehyde emissions, raising concerns about indoor air quality and environmental toxicity. Sustainable sourcing and low-emission certifications such as FSC and CARB-compliant products are critical factors influencing the environmental impact of both materials in furniture manufacturing.
Aesthetic Appeal and Finishing Options
Engineered wood offers a smoother, more consistent surface ideal for high-quality finishes like veneers and laminates, enhancing its aesthetic appeal in modern furniture design. Particle board typically has a rougher texture and lower density, limiting finishing options to basic paints or thin laminates that may chip or peel over time. Choosing engineered wood allows for more refined detailing and a durable, attractive finish suited for premium furniture pieces.
Maintenance and Longevity
Engineered wood offers superior durability and requires minimal maintenance compared to particle board, which is more susceptible to moisture damage and warping. Regular cleaning with a soft cloth and avoiding excessive water exposure prolongs the life of engineered wood furniture. Particle board furniture typically has a shorter lifespan due to its lower density and vulnerability to chipping and swelling over time.
Best Use Cases for Engineered Wood and Particle Board
Engineered wood is best used for furniture requiring durability and structural integrity, such as cabinets, shelves, and flooring, due to its layered construction and resistance to warping. Particle board suits budget-friendly furniture like flat-pack desks and lightweight shelving where cost efficiency and smooth finishes are prioritized over strength. Choosing engineered wood enhances longevity in high-stress applications, while particle board is ideal for temporary or decorative pieces with minimal load requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Furniture
Engineered wood offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and a more attractive finish compared to particle board, making it ideal for long-lasting furniture pieces. Particle board is cost-effective and lightweight but less durable, suitable for budget-friendly or temporary furniture. Selecting the right material depends on your priorities for strength, aesthetics, and budget in furniture construction.
Engineered wood vs Particle board Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com