Overpronation occurs when the foot excessively rolls inward during walking or running, causing uneven pressure and potential strain on the ankles and knees. Supination, in contrast, is characterized by the foot rolling outward, leading to insufficient shock absorption and increased risk of ankle sprains. Proper footwear that addresses each condition can improve gait, reduce injury risk, and enhance overall foot stability.
Table of Comparison
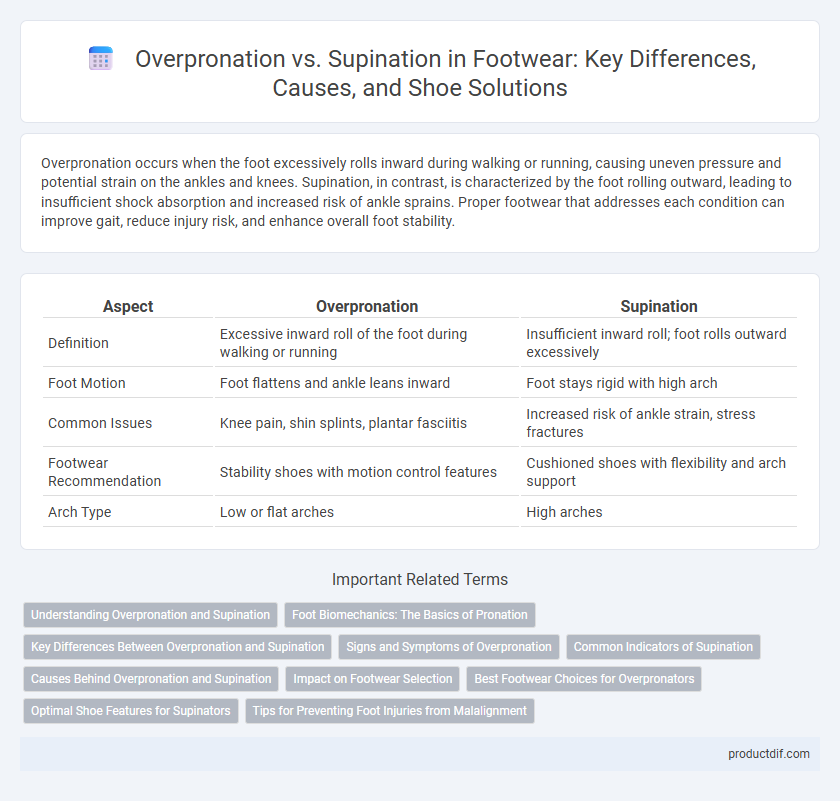
| Aspect | Overpronation | Supination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive inward roll of the foot during walking or running | Insufficient inward roll; foot rolls outward excessively |
| Foot Motion | Foot flattens and ankle leans inward | Foot stays rigid with high arch |
| Common Issues | Knee pain, shin splints, plantar fasciitis | Increased risk of ankle strain, stress fractures |
| Footwear Recommendation | Stability shoes with motion control features | Cushioned shoes with flexibility and arch support |
| Arch Type | Low or flat arches | High arches |
Understanding Overpronation and Supination
Overpronation occurs when the foot rolls inward excessively during walking or running, leading to increased pressure on the inner edge of the foot. Supination, also known as underpronation, involves insufficient inward roll, causing weight to be placed on the outer edge of the foot. Recognizing these gait patterns is crucial for selecting appropriate footwear that provides optimal support and reduces the risk of injury.
Foot Biomechanics: The Basics of Pronation
Pronation refers to the natural inward roll of the foot during walking or running, essential for shock absorption and balance. Overpronation occurs when the foot rolls excessively inward, often leading to increased strain on the arch and potential injuries, while supination involves insufficient inward roll, causing the foot to remain rigid and absorb less impact. Understanding foot biomechanics helps in selecting appropriate footwear that supports the natural pronation pattern, enhancing comfort and reducing the risk of musculoskeletal issues.
Key Differences Between Overpronation and Supination
Overpronation involves excessive inward rolling of the foot during walking or running, leading to increased stress on the ankle and knee joints, whereas supination is characterized by insufficient inward roll, causing the foot to roll outward and placing strain on the outer edges. Overpronators often experience flat feet and require shoes with enhanced medial support, while supinators typically have high arches needing cushioned footwear to absorb impact. Understanding these biomechanical differences is crucial for selecting appropriate footwear that enhances stability, prevents injuries, and improves athletic performance.
Signs and Symptoms of Overpronation
Overpronation is characterized by excessive inward rolling of the foot during walking or running, often leading to uneven wear on the inner edge of shoes and increased strain on the arch and ankle. Common signs include flat feet, pain in the inner foot or shin splints, and frequent ankle sprains due to instability. Identifying these symptoms early can help in selecting appropriate footwear or orthotic support to correct gait mechanics and prevent injury.
Common Indicators of Supination
Supination is characterized by the outward roll of the foot during normal motion, often resulting in excessive pressure on the outer edges of the feet and heels. Common indicators include high arches, uneven wear on the outer sole of shoes, and frequent ankle instability or sprains. This gait pattern can lead to increased risk of stress fractures, plantar fasciitis, and tight Achilles tendons, making proper footwear with neutral or cushioned support essential.
Causes Behind Overpronation and Supination
Overpronation is primarily caused by weak or imbalanced foot muscles, flat arches, and improper gait mechanics, leading to excessive inward rolling of the foot during walking or running. Supination often results from high arches, tight Achilles tendons, or poor shock absorption, causing the foot to roll outward excessively. Both conditions influence footwear choice, necessitating shoes with specific support features to correct alignment and prevent injury.
Impact on Footwear Selection
Overpronation causes excessive inward rolling of the foot, requiring motion control shoes with enhanced medial support and stability features to prevent injury. Supination, characterized by outward foot roll, demands footwear with cushioned midsoles and flexible outsoles to absorb shock and enhance adaptability. Choosing the right shoe based on foot strike patterns significantly improves comfort, reduces wear, and prevents common foot ailments.
Best Footwear Choices for Overpronators
Overpronators benefit from stability or motion control shoes designed to correct inward rolling of the foot, providing enhanced arch support and medial posts to prevent excessive pronation. Footwear brands like Brooks, ASICS, and New Balance offer specialized running shoes with firm midsoles and structured cushioning that improve gait alignment and reduce injury risk. Selecting shoes with reinforced heel counters and durable outsoles ensures added stability and durability for overpronators during high-impact activities.
Optimal Shoe Features for Supinators
Supinators benefit from shoes featuring enhanced cushioning to absorb impact and reduce pressure on the outer foot. Lightweight materials combined with flexible soles promote natural foot movement and prevent strain during walking or running. A wider base and supportive arch design help maintain balance and prevent excessive outward rolling of the foot.
Tips for Preventing Foot Injuries from Malalignment
Proper footwear with adequate arch support and cushioning helps correct overpronation and supination, reducing strain on the feet and preventing injuries. Custom orthotics tailored to individual gait patterns provide stability and realign foot mechanics during walking or running. Regular strengthening exercises targeting foot and ankle muscles improve alignment and enhance overall foot function, minimizing the risk of malalignment-related injuries.
Overpronation vs Supination Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com