Chemical peels use acids like glycolic or salicylic acid to exfoliate and remove damaged skin layers, promoting cell turnover and revealing smoother, clearer skin. Enzyme peels rely on natural enzymes from fruits such as papaya or pumpkin to gently break down dead skin cells without irritation, making them ideal for sensitive skin types. Both treatments improve skin texture and tone, but chemical peels offer more intense exfoliation, while enzyme peels provide a milder, more soothing alternative.
Table of Comparison
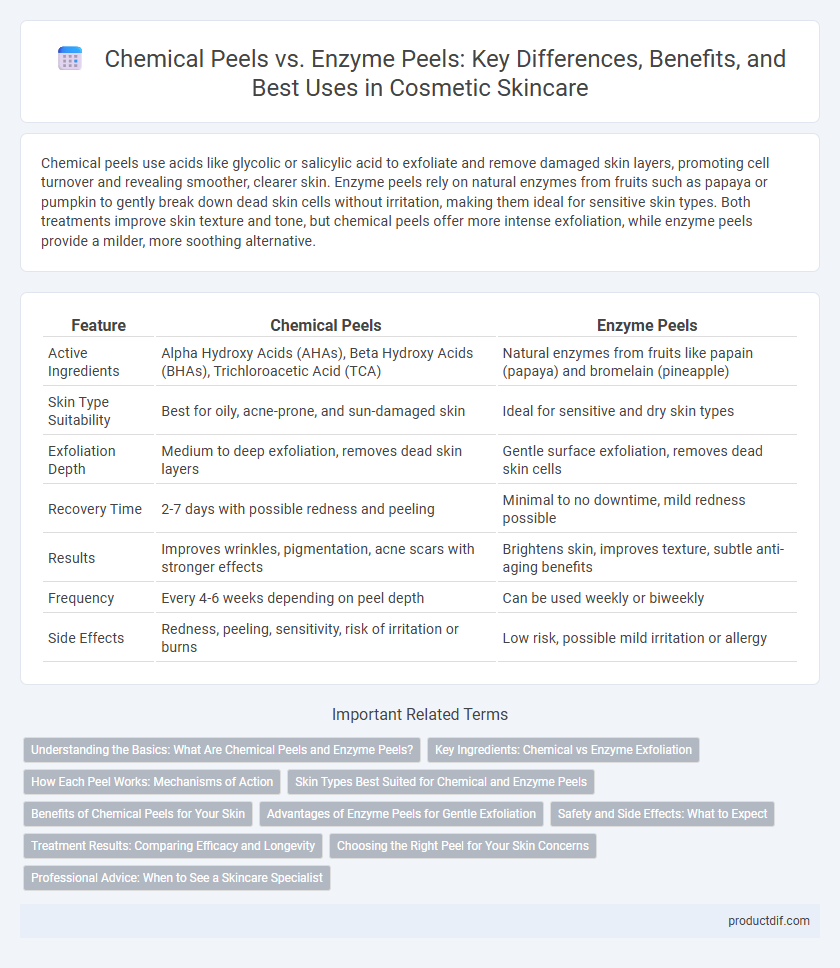
| Feature | Chemical Peels | Enzyme Peels |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredients | Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs), Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs), Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA) | Natural enzymes from fruits like papain (papaya) and bromelain (pineapple) |
| Skin Type Suitability | Best for oily, acne-prone, and sun-damaged skin | Ideal for sensitive and dry skin types |
| Exfoliation Depth | Medium to deep exfoliation, removes dead skin layers | Gentle surface exfoliation, removes dead skin cells |
| Recovery Time | 2-7 days with possible redness and peeling | Minimal to no downtime, mild redness possible |
| Results | Improves wrinkles, pigmentation, acne scars with stronger effects | Brightens skin, improves texture, subtle anti-aging benefits |
| Frequency | Every 4-6 weeks depending on peel depth | Can be used weekly or biweekly |
| Side Effects | Redness, peeling, sensitivity, risk of irritation or burns | Low risk, possible mild irritation or allergy |
Understanding the Basics: What Are Chemical Peels and Enzyme Peels?
Chemical peels utilize acids like glycolic, salicylic, or trichloroacetic acid to exfoliate the skin by removing dead cells and promoting collagen production, resulting in smoother texture and improved tone. Enzyme peels use natural enzymes from fruits such as papaya or pineapple to gently dissolve dead skin cells without causing irritation, making them suitable for sensitive skin types. Both treatments target skin renewal but differ in their exfoliation methods and intensity, affecting recovery time and suitability for various skin concerns.
Key Ingredients: Chemical vs Enzyme Exfoliation
Chemical peels primarily utilize alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) such as salicylic acid to dissolve dead skin cells and promote cell turnover. Enzyme peels rely on natural plant-derived enzymes, including papain from papaya and bromelain from pineapple, to gently break down protein bonds in the outer skin layer without harsh irritation. Both exfoliation methods target skin renewal but differ in their key ingredients and mechanisms, making enzyme peels ideal for sensitive skin while chemical peels are favored for deeper exfoliation.
How Each Peel Works: Mechanisms of Action
Chemical peels use acids like glycolic, salicylic, or trichloroacetic acid to exfoliate the skin by breaking down dead skin cells and stimulating collagen production, promoting cell turnover and revealing fresher, smoother skin. Enzyme peels rely on natural enzymes from fruits such as papaya, pineapple, or pumpkin to gently dissolve dead skin without irritation, making them ideal for sensitive skin types. The controlled epithelial exfoliation by chemical peels contrasts with the enzyme peels' targeted breakdown of keratin protein, resulting in different depths of exfoliation and skin renewal.
Skin Types Best Suited for Chemical and Enzyme Peels
Chemical peels are best suited for individuals with oily, acne-prone, or sun-damaged skin as they penetrate deeply to exfoliate and renew the skin's surface, effectively reducing hyperpigmentation and fine lines. Enzyme peels are ideal for sensitive or dry skin types because they use natural enzymes from fruits like papaya or pineapple to gently dissolve dead skin cells without causing irritation or excessive dryness. Choosing the right peel depends on skin sensitivity, with chemical peels offering stronger exfoliation benefits for resilient skin and enzyme peels providing a milder alternative for delicate complexions.
Benefits of Chemical Peels for Your Skin
Chemical peels effectively target deeper layers of the skin, promoting collagen production and improving texture, tone, and pigmentation issues. They provide significant benefits for acne scars, sun damage, and fine lines by accelerating skin cell turnover. This controlled exfoliation results in a smoother, brighter complexion and enhanced skin rejuvenation compared to enzyme peels.
Advantages of Enzyme Peels for Gentle Exfoliation
Enzyme peels offer a gentle exfoliation by utilizing natural enzymes like papain and bromelain to dissolve dead skin cells without causing irritation or redness common with chemical peels. This makes enzyme peels ideal for sensitive skin types and those prone to inflammation, promoting a smoother, brighter complexion with minimal downtime. Enzyme peels also support enzymatic removal of dead tissue while preserving the skin's natural moisture balance, enhancing overall skin health and radiance.
Safety and Side Effects: What to Expect
Chemical peels typically involve acids such as glycolic or salicylic acid, which can cause redness, irritation, and peeling during recovery, especially for sensitive skin types. Enzyme peels use natural enzymes from fruits like papaya or pineapple, providing a gentler exfoliation with minimal risk of adverse reactions, making them safer for sensitive or reactive skin. Both treatments require proper post-peel care to prevent complications such as hyperpigmentation or infection.
Treatment Results: Comparing Efficacy and Longevity
Chemical peels utilize acids like glycolic, salicylic, or trichloroacetic acid to exfoliate deeper layers of skin, resulting in more dramatic improvements in texture, pigmentation, and acne scars with longer-lasting effects. Enzyme peels, composed of natural enzymes such as papain or bromelain, offer gentler exfoliation targeting surface dead cells, making them ideal for sensitive skin with quicker but milder results. While chemical peels often require downtime, their efficacy in stimulating collagen production and skin renewal typically yields superior longevity in treatment outcomes compared to enzyme peels.
Choosing the Right Peel for Your Skin Concerns
Chemical peels utilize acids like glycolic or salicylic acid to exfoliate dead skin cells, effectively targeting acne, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines for deeper skin renewal. Enzyme peels harness natural fruit enzymes such as papain or bromelain to gently dissolve dead skin without irritation, making them ideal for sensitive or reactive skin types. Selecting the right peel depends on your skin's tolerance, desired results, and specific concerns, with chemical peels offering more intense resurfacing and enzyme peels providing mild, soothing exfoliation.
Professional Advice: When to See a Skincare Specialist
Consulting a skincare specialist is crucial for determining whether chemical peels or enzyme peels suit your skin type and concerns. Professionals assess factors such as skin sensitivity, underlying conditions, and desired results to recommend the safest and most effective treatment. Regular evaluations by a dermatologist help prevent adverse reactions and ensure optimal skin rejuvenation outcomes.
Chemical Peels vs Enzyme Peels Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com