Aluminized steel bakeware offers excellent heat distribution and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for even cooking and durability. Carbon steel bakeware heats up quickly and provides superior responsiveness to temperature changes, favored for tasks requiring precise control. Both materials are lightweight and strong but aluminized steel tends to outlast carbon steel due to its protective aluminum-silicon coating.
Table of Comparison
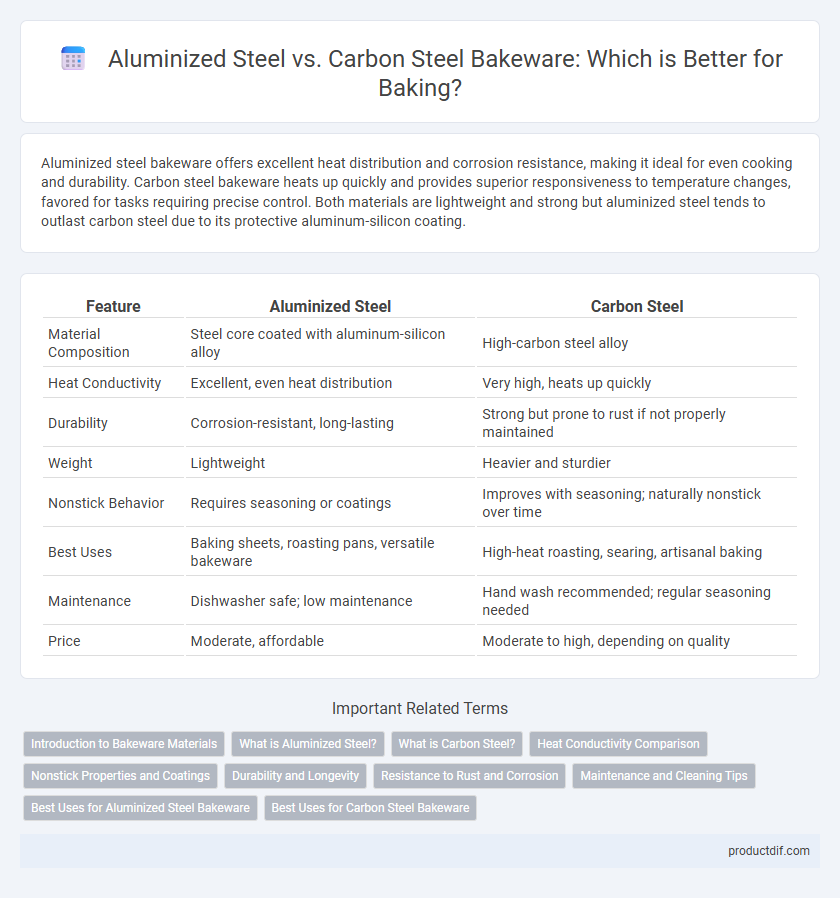
| Feature | Aluminized Steel | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Steel core coated with aluminum-silicon alloy | High-carbon steel alloy |
| Heat Conductivity | Excellent, even heat distribution | Very high, heats up quickly |
| Durability | Corrosion-resistant, long-lasting | Strong but prone to rust if not properly maintained |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier and sturdier |
| Nonstick Behavior | Requires seasoning or coatings | Improves with seasoning; naturally nonstick over time |
| Best Uses | Baking sheets, roasting pans, versatile bakeware | High-heat roasting, searing, artisanal baking |
| Maintenance | Dishwasher safe; low maintenance | Hand wash recommended; regular seasoning needed |
| Price | Moderate, affordable | Moderate to high, depending on quality |
Introduction to Bakeware Materials
Aluminized steel offers excellent heat conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for bakeware that requires consistent temperature distribution. Carbon steel, known for its superior strength and durability, provides faster heat-up times but requires seasoning to maintain its non-stick properties. Both materials are favored for their performance in professional and home baking environments, with durability and heat retention as key considerations.
What is Aluminized Steel?
Aluminized steel is a type of bakeware material composed of carbon steel coated with an aluminum-silicon alloy, providing excellent heat conductivity and corrosion resistance. It combines the strength and durability of carbon steel with the non-reactive, rust-resistant properties of aluminum, making it ideal for baking applications. This material ensures even heat distribution and improved longevity compared to traditional steel bakeware.
What is Carbon Steel?
Carbon steel is a durable metal alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, known for its excellent heat conduction and retention, making it ideal for bakeware. This material offers superior strength and resistance to warping compared to aluminized steel, allowing for even cooking and long-lasting performance. Carbon steel bakeware typically requires seasoning to develop a natural non-stick surface and prevent rusting.
Heat Conductivity Comparison
Aluminized steel offers moderate heat conductivity, providing even heat distribution ideal for consistent baking results. Carbon steel conducts heat faster and more efficiently, allowing for quicker temperature response and superior browning. Choosing between aluminized and carbon steel bakeware depends on the desired balance between heat retention and rapid heating performance.
Nonstick Properties and Coatings
Aluminized steel bakeware offers moderate nonstick properties due to its aluminum coating, providing even heat distribution and resistance to rust. Carbon steel, often uncoated, requires seasoning to develop a natural nonstick surface, enhancing durability but needing maintenance to prevent rust. Nonstick coatings on aluminized steel improve release and cleaning, while carbon steel's traditional seasoning offers a chemical-free alternative with superior heat conduction.
Durability and Longevity
Aluminized steel bakeware offers superior corrosion resistance and heat distribution, ensuring long-lasting durability under frequent baking conditions. Carbon steel is highly durable and provides excellent heat conductivity but requires careful maintenance to prevent rust and extend its lifespan. Choosing aluminized steel enhances bakeware longevity through its protective coating, while carbon steel demands seasoning for optimal performance and durability.
Resistance to Rust and Corrosion
Aluminized steel bakeware features a protective aluminum-silicon alloy coating that significantly enhances resistance to rust and corrosion compared to carbon steel, which is more prone to oxidation without proper seasoning or coating. Carbon steel requires regular maintenance, such as oiling, to prevent rust, whereas aluminized steel provides a durable, rust-resistant surface ideal for longevity in baking applications. This makes aluminized steel a preferred choice for users seeking low-maintenance, corrosion-resistant bakeware.
Maintenance and Cleaning Tips
Aluminized steel bakeware requires gentle cleaning with warm soapy water and a soft sponge to maintain its corrosion-resistant coating, avoiding abrasive pads that can damage the surface. Carbon steel bakeware benefits from immediate hand washing, thorough drying, and occasional seasoning with oil to prevent rust and enhance its non-stick properties. Both materials should be stored in dry places to extend their lifespan and maintain optimal baking performance.
Best Uses for Aluminized Steel Bakeware
Aluminized steel bakeware excels in even heat distribution and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for roasting pans and cookie sheets used at high temperatures. Its durability and non-reactive surface prevent flavor alteration, perfect for baking breads and roasting meats. The bakeware's ability to withstand frequent use without warping ensures consistent results in professional and home kitchens alike.
Best Uses for Carbon Steel Bakeware
Carbon steel bakeware excels in heat conductivity and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature baking and roasting tasks. This material is preferred for pizza pans, baking sheets, and bread pans where rapid, even heat distribution is crucial for achieving crispy crusts and uniform browning. Its natural non-stick patina develops over time, enhancing performance for repeated use in professional and home kitchens.
Aluminized Steel vs Carbon Steel Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com