Rear-facing car seats provide superior protection for infants and toddlers by supporting the head, neck, and spine in the event of a collision, reducing the risk of serious injury. Forward-facing seats are designed for older children, offering secure harness systems that accommodate growth while promoting proper posture. Choosing the appropriate seat based on age, weight, and height guidelines ensures optimal safety during every car ride.
Table of Comparison
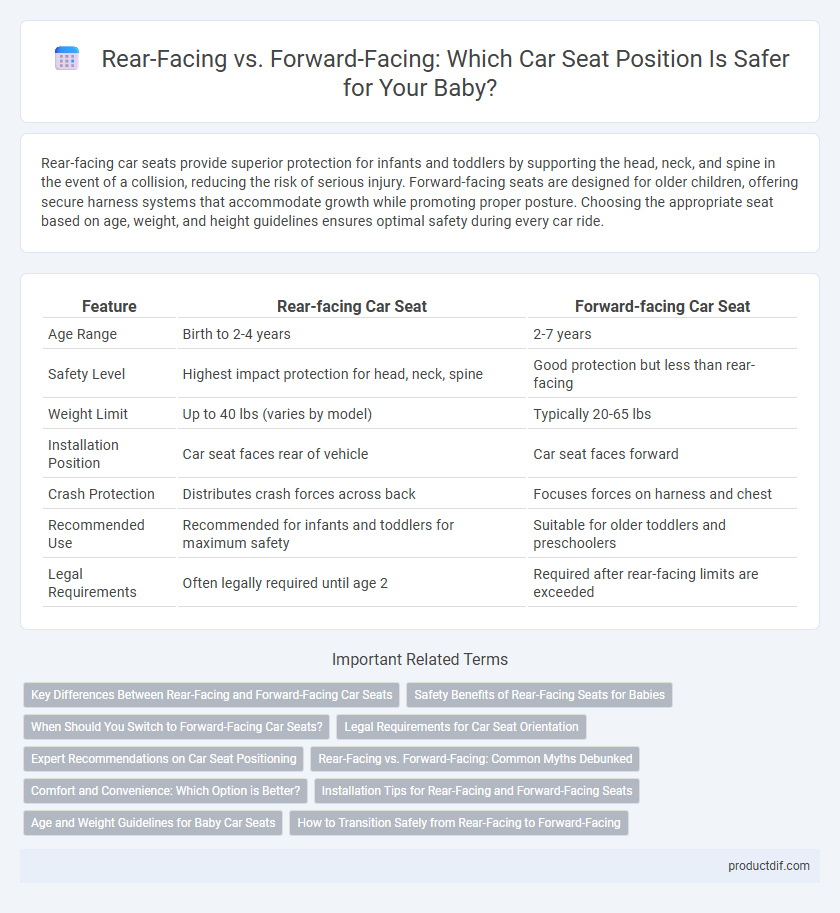
| Feature | Rear-facing Car Seat | Forward-facing Car Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Age Range | Birth to 2-4 years | 2-7 years |
| Safety Level | Highest impact protection for head, neck, spine | Good protection but less than rear-facing |
| Weight Limit | Up to 40 lbs (varies by model) | Typically 20-65 lbs |
| Installation Position | Car seat faces rear of vehicle | Car seat faces forward |
| Crash Protection | Distributes crash forces across back | Focuses forces on harness and chest |
| Recommended Use | Recommended for infants and toddlers for maximum safety | Suitable for older toddlers and preschoolers |
| Legal Requirements | Often legally required until age 2 | Required after rear-facing limits are exceeded |
Key Differences Between Rear-Facing and Forward-Facing Car Seats
Rear-facing car seats provide enhanced protection for infants and toddlers by supporting the head, neck, and spine in the event of a collision, significantly reducing injury risk. Forward-facing car seats are designed for older children who have outgrown rear-facing limits, offering harness systems that secure the child while allowing greater visibility and mobility. Choosing the appropriate seat depends on the child's age, weight, and height, with safety guidelines recommending rear-facing usage until at least age two or the maximum rear-facing size limit is reached.
Safety Benefits of Rear-Facing Seats for Babies
Rear-facing car seats provide superior protection for babies by supporting the head, neck, and spine during sudden stops or collisions. Research from the American Academy of Pediatrics shows that rear-facing seats reduce the risk of severe injury by up to 75% compared to forward-facing seats. Ensuring babies remain rear-facing until at least age two maximizes safety benefits during critical early development stages.
When Should You Switch to Forward-Facing Car Seats?
Switching to a forward-facing car seat is recommended when a child reaches the height, weight, and age limits specified by the car seat manufacturer, often around 2 years old or older. Rear-facing seats provide optimal protection for a child's developing neck and spine, reducing the risk of serious injury during a crash by distributing crash forces more evenly. Safety experts and organizations like the American Academy of Pediatrics advise keeping children rear-facing as long as possible to maximize safety benefits before transitioning to forward-facing seats.
Legal Requirements for Car Seat Orientation
Legal requirements for car seat orientation vary by jurisdiction, typically mandating rear-facing seats for infants and toddlers up to at least 2 years of age to maximize safety. Forward-facing seats are generally permitted only after the child exceeds the rear-facing weight or height limits specified by local laws. Compliance with these regulations ensures optimal protection in the event of a collision, reducing the risk of injury for young passengers.
Expert Recommendations on Car Seat Positioning
Experts recommend keeping children in rear-facing car seats until at least age 2 or until they reach the maximum height and weight limit for the seat, as this position offers superior protection for the head, neck, and spine in crashes. Forward-facing seats with a harness are advised only after outgrowing rear-facing limits, typically for toddlers and preschoolers up to age 5 or beyond depending on the specific model. Pediatric safety organizations emphasize that proper seat positioning significantly reduces the risk of serious injury during car accidents.
Rear-Facing vs. Forward-Facing: Common Myths Debunked
Rear-facing car seats provide superior protection for infants and toddlers by supporting the head, neck, and spine during collisions, contrary to myths claiming forward-facing seats offer equal safety. Experts recommend keeping children rear-facing until at least age two or until they exceed the height and weight limits set by the car seat manufacturer. Studies from the American Academy of Pediatrics show rear-facing seats reduce fatal injury risk by up to 75% compared to forward-facing seats.
Comfort and Convenience: Which Option is Better?
Rear-facing car seats provide superior comfort for infants and toddlers by offering better head and neck support, reducing the impact of sudden movements during travel. Forward-facing seats, while designed for older children, offer more convenience with easier access and adjustable features that accommodate growth. Choosing between rear-facing and forward-facing depends on balancing optimal safety and comfort with ease of use during daily routines.
Installation Tips for Rear-Facing and Forward-Facing Seats
Proper installation of rear-facing car seats requires securing the base firmly using either the vehicle's LATCH system or seat belt, ensuring the seat reclines at the manufacturer-recommended angle to support an infant's head and airway. Forward-facing seats should be installed using the top tether anchor in addition to the lower LATCH connectors or seat belt, minimizing seat movement and enhancing child safety during impact. Checking the car seat's manual for specific installation instructions and conducting a tightness test--where the seat should not move more than an inch side to side or front to back--ensures both rear-facing and forward-facing seats are correctly installed.
Age and Weight Guidelines for Baby Car Seats
Rear-facing baby car seats are recommended from birth up to at least 2 years old or until the child reaches the maximum weight limit specified by the seat, usually between 20 to 40 pounds. Forward-facing seats are suitable once the child outgrows the rear-facing limits, typically starting around age 2 and weighing between 22 to 65 pounds depending on the model. Following these age and weight guidelines ensures optimal safety and compliance with child passenger protection standards.
How to Transition Safely from Rear-Facing to Forward-Facing
Transition safely from rear-facing to forward-facing by following the American Academy of Pediatrics' recommendation to keep your child rear-facing until at least age 2 or the maximum height and weight limit of the car seat. Ensure the forward-facing car seat is installed tightly using a seat belt or LATCH system and that the harness fits snugly at or above the child's shoulders. Always check the car seat manufacturer's guidelines for specific weight, height limits, and proper harness adjustment to maximize protection during the transition.
Rear-facing vs Forward-facing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com